Heart Disease: A Comprehensive Guide to Causes, Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease (CVD), is the leading cause of death worldwide. It refers to a group of disorders that affect the heart and blood vessels, including coronary artery disease, heart attacks, heart failure, arrhythmias, and congenital heart defects. According to global health estimates, millions of people die every year due to heart-related conditions, making it a major public health concern across both developed and developing nations.
Modern lifestyles characterized by poor dietary habits, physical inactivity, chronic stress, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption have significantly increased the risk of heart disease. However, the good news is that many forms of heart disease are preventable through lifestyle changes, early diagnosis, and appropriate medical treatment.
This article provides an in-depth, evidence-based overview of heart disease, covering its types, causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, diet plans, exercise recommendations, mental health connections, and future trends in cardiovascular care.
1. Understanding the Heart and Cardiovascular System
The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located slightly left of the center of the chest. Its primary function is to pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients while removing waste products such as carbon dioxide.
Key Components of the Cardiovascular System
- Heart – pumps blood
- Blood vessels – arteries, veins, and capillaries
- Blood – carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells
A healthy cardiovascular system ensures efficient circulation. When any part of this system is damaged or blocked, heart disease can occur.
2. Types of Heart Disease
2.1 Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Coronary artery disease is the most common type of heart disease. It occurs when the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis).
2.2 Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction)
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is completely blocked, usually by a blood clot. This can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle.
2.3 Heart Failure
Heart failure does not mean the heart has stopped working. It means the heart cannot pump blood efficiently to meet the body’s needs.
2.4 Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia refers to irregular heartbeats, which can be too fast, too slow, or erratic.
2.5 Congenital Heart Disease
These are structural heart defects present at birth.
2.6 Valvular Heart Disease
Occurs when one or more heart valves do not function properly.
3. Causes of Heart Disease
Heart disease develops due to a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Major Causes Include:
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup)
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Chronic stress
- Excessive alcohol consumption
4. Risk Factors for Heart Disease
4.1 Modifiable Risk Factors
- Poor diet
- Lack of exercise
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Stress
4.2 Non-Modifiable Risk Factors
- Age
- Gender
- Family history
- Genetics
Understanding risk factors allows individuals to take preventive action early.
5. Symptoms of Heart Disease
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity of heart disease.
Common Symptoms:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or fainting
- Irregular heartbeat
- Swelling in legs, ankles, or feet
Warning Signs of a Heart Attack:
- Intense chest pressure
- Pain radiating to arm, neck, or jaw
- Nausea
- Cold sweats
Immediate medical attention is critical.
6. Diagnosis of Heart Disease
Doctors use various tests to diagnose heart disease:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Stress test
- Blood tests
- Coronary angiography
- CT and MRI scans
Early diagnosis can save lives.
7. Treatment Options for Heart Disease
7.1 Lifestyle Changes
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Stress management
- Smoking cessation
7.2 Medications
- Blood pressure medications
- Cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins)
- Blood thinners
- Beta-blockers
7.3 Medical Procedures
- Angioplasty
- Stent placement
- Bypass surgery
- Pacemakers
8. Diet for Heart Health
A heart-healthy diet plays a crucial role in prevention and management.
Recommended Foods:
- Fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean proteins
- Healthy fats (olive oil, nuts)
Foods to Avoid:
- Trans fats
- Excess sugar
- Processed foods
- Excess salt
9. Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart.
Recommended Exercises:
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Yoga
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
10. Mental Health and Heart Disease
Stress, anxiety, and depression significantly impact heart health.
Stress Management Techniques:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing
- Adequate sleep
- Social support
11. Heart Disease in Women
Heart disease symptoms in women may differ from men and are often underdiagnosed.
12. Heart Disease in Men
Men are generally at higher risk at a younger age.
13. Heart Disease in Children
Congenital heart defects are the most common form in children.
14. Prevention of Heart Disease
Key Prevention Strategies:
- Maintain healthy weight
- Control blood pressure
- Manage diabetes
- Quit smoking
15. Role of Technology in Heart Care
- Wearable devices
- Telemedicine
- AI-based diagnostics
16. Myths and Facts About Heart Disease
Myth: Heart disease affects only older people.
Fact: It can affect people of all ages.
17. Global Impact of Heart Disease
Heart disease places a heavy burden on healthcare systems worldwide.
18. Future of Heart Disease Treatment
Advances in genetics, personalized medicine, and minimally invasive procedures offer hope.
19. Living with Heart Disease
With proper care, many people live long and fulfilling lives.
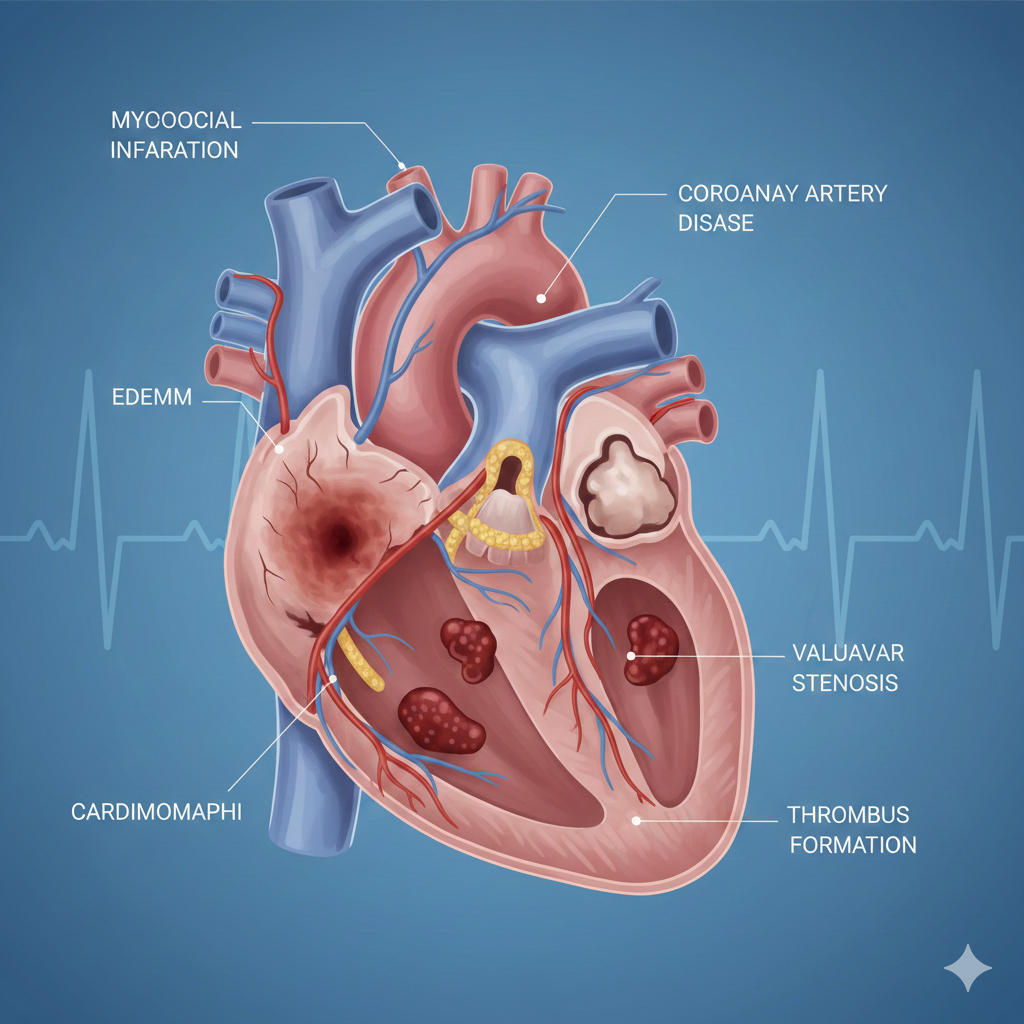
Heart Disease Treatment: Medical Care, Exercise, Yoga, and Ayurvedic Approaches
Introduction
Heart disease treatment requires a comprehensive, long-term approach that combines modern medical care with healthy lifestyle practices. For UK and US audiences, evidence-based medical treatment remains the foundation of heart disease management. However, complementary approaches such as exercise, yoga, stress reduction, and selected Ayurvedic practices are increasingly recognized for their supportive role in improving heart health and overall well-being.
This article focuses on treatment and management, not cures. It explains how medical therapy, physical activity, yoga, and Ayurvedic methods can work together safely and responsibly to support people living with heart disease.
Important Disclaimer: The information provided here is for educational purposes only. Ayurvedic and alternative practices are supportive in nature and should never replace prescribed medical treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare professional.
1. Goals of Heart Disease Treatment
The primary goals of heart disease treatment include:
- Reducing symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath
- Preventing disease progression
- Lowering the risk of heart attack and stroke
- Improving quality of life
- Increasing life expectancy
Effective treatment plans are individualized based on the type of heart disease, age, overall health, and risk factors.
2. Medical Treatment for Heart Disease
2.1 Medications Commonly Used
Medical therapy is the cornerstone of heart disease treatment in the UK and US.
- Antiplatelet drugs (e.g., aspirin): Reduce clot formation
- Statins: Lower LDL cholesterol and stabilize plaques
- Beta-blockers: Reduce heart workload and control heart rate
- ACE inhibitors / ARBs: Improve blood flow and lower blood pressure
- Diuretics: Reduce fluid buildup in heart failure
Medications must be taken exactly as prescribed.
2.2 Medical Procedures and Interventions
For moderate to severe cases, procedures may be required:
- Angioplasty and stent placement
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- Pacemaker implantation
- Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs)
These treatments significantly reduce mortality when used appropriately.
3. Role of Exercise in Heart Disease Treatment
3.1 Why Exercise Is Essential
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, lowers blood pressure, improves cholesterol levels, and reduces stress.
Clinical guidelines in the UK and US strongly recommend structured physical activity as part of cardiac rehabilitation.
3.2 Recommended Exercises for Heart Patients
Walking
- Safest and most accessible exercise
- Improves cardiovascular endurance
Cycling
- Low-impact option
- Improves heart efficiency
Swimming
- Excellent for joint-friendly cardio
- Enhances lung capacity
Light Resistance Training
- Improves muscle strength
- Supports metabolic health
Recommended duration:
- 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
Always start gradually and follow medical advice.
4. Cardiac Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehabilitation is a medically supervised program that includes:
- Exercise training
- Nutrition counseling
- Stress management
- Education on heart-healthy living
These programs significantly reduce hospital readmission rates.
5. Yoga for Heart Disease Management
5.1 How Yoga Supports Heart Health
Yoga improves heart health by:
- Reducing stress hormones
- Lowering blood pressure
- Improving breathing efficiency
- Enhancing emotional balance
Scientific studies suggest yoga complements conventional treatment.
5.2 Recommended Yoga Practices
Gentle Asanas
- Tadasana (Mountain Pose)
- Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose)
- Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose)
Breathing Techniques (Pranayama)
- Anulom Vilom
- Bhramari
- Deep diaphragmatic breathing
Yoga should be practiced under guidance, especially for heart patients.
6. Stress Management as Treatment
Chronic stress contributes to hypertension and heart rhythm disturbances.
Effective Stress-Reduction Methods:
- Meditation
- Mindfulness practices
- Adequate sleep
- Social support
Mental well-being is a critical component of heart disease treatment.
7. Ayurvedic Approach to Heart Disease Treatment
7.1 Ayurveda as a Supportive System
Ayurveda is a traditional system of medicine that emphasizes balance between body, mind, and lifestyle. In Western healthcare, Ayurveda is considered complementary rather than curative.
7.2 Common Ayurvedic Herbs Used for Heart Support
Arjuna (Terminalia arjuna)
- Traditionally used to support heart muscle function
- Studied for cholesterol and blood pressure support
Ashwagandha
- Helps reduce stress and anxiety
- Supports hormonal balance
Garlic
- Widely accepted in Western medicine
- Supports cholesterol management
Turmeric (Curcumin)
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Supports vascular health
No herb should be taken without medical supervision.
8. Ayurvedic Lifestyle Practices
Ayurvedic treatment focuses heavily on lifestyle:
- Regular sleep-wake cycle
- Balanced meals
- Avoiding excessive stimulation
- Daily movement
These practices align well with modern heart-health guidelines.
9. Diet as Part of Treatment
A heart-healthy diet is a key component of treatment.
Recommended Dietary Patterns:
- Mediterranean diet
- DASH diet
- Plant-forward eating
Foods to Limit:
- Processed foods
- Trans fats
- Excess sodium
- Added sugars
10. Integrating Medical and Complementary Treatments
The safest approach is integrative care, where medical treatment remains primary and complementary methods support recovery and well-being.
Open communication between patients and healthcare providers is essential.
11. Safety Considerations and Warnings
- Never stop prescribed medication
- Avoid unverified supplements
- Report symptoms immediately
- Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol regularly
12. Living Well with Heart Disease
With appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments, many individuals with heart disease live long, productive lives.
Consistency, education, and professional guidance are key to success.
Conclusion
Heart disease treatment is most effective when it combines modern medical care with supportive lifestyle practices such as exercise, yoga, stress management, and carefully supervised Ayurvedic approaches. While alternative therapies may enhance well-being, they must always be used responsibly and alongside evidence-based medical treatment.
A balanced, informed, and integrative approach offers the best outcomes for heart disease patients.
Medical Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not intended as a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
🔹 Paragraph 1 – General Heart Health (Introduction)
Paragraph text:
Heart disease treatment involves a combination of medical care, healthy lifestyle choices, and long-term prevention strategies. Understanding cardiovascular health from reliable sources helps individuals manage risk factors, improve daily habits, and make informed decisions about treatment and recovery.
Internal link
👉 Read more: Health Guide Me
https://healthguideme.com/
🔹 Paragraph 2 – Medical & Metabolic Risk Factors
Paragraph text:
Heart disease is often closely linked with metabolic conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance, and liver disorders. Poor liver health can increase inflammation and cardiovascular risk, making early identification of genetic and lifestyle factors especially important in long-term heart disease management.
Internal link
👉 Related article: Fatty Liver Disease and Genetics
https://healthguideme.com/fatty-liver-disease-genetics/
🔹 Paragraph 3 – Lifestyle & Quality of Life
Paragraph text:
Living with heart disease can affect overall quality of life, including energy levels, emotional balance, and personal relationships. Maintaining good cardiovascular health supports not only physical strength but also confidence, intimacy, and mental well-being.
Internal link
👉 Learn more: Sex Life and Overall Health
https://healthguideme.com/sex-life-and-health/
🔹 Paragraph 1 – Global Heart Disease Overview
Paragraph text:
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. Understanding its global impact, risk factors, and prevention strategies helps individuals recognize the seriousness of cardiovascular disease and the importance of early intervention.
External link
👉 World Health Organization – Cardiovascular Diseases
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
🔹 Paragraph 2 – UK Medical Guidance
Paragraph text:
In the United Kingdom, heart disease management is guided by evidence-based clinical recommendations that focus on early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and long-term medical care. Following national health guidelines can significantly reduce complications and improve survival rates.
External link
👉 NHS – Coronary Heart Disease
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronary-heart-disease/
🔹 Paragraph 3 – US Heart Disease Treatment Standards
Paragraph text:
In the United States, heart disease treatment emphasizes prevention, medication adherence, physical activity, and regular medical monitoring. Public health organizations provide detailed resources to help patients understand symptoms, treatments, and recovery strategies.
External link (paragraph යටින්):
👉 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Heart Disease
https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/
🔹 Paragraph 4 – Medical Education & Symptoms
Paragraph text:
Recognizing the early symptoms of heart disease is critical for timely treatment. Chest discomfort, shortness of breath, fatigue, and irregular heartbeat are common warning signs that require medical attention.
External link
👉 Mayo Clinic – Heart Disease Symptoms & Causes
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20353118
🔹 Paragraph 5 – Lifestyle & Prevention Research
Paragraph text:
Scientific research consistently shows that healthy lifestyle choices such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, stress management, and smoking cessation play a major role in preventing heart disease and supporting treatment outcomes.
External link
👉 American Heart Association – Prevention & Healthy Living
https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living
| Old phrase | Replace with |
|---|---|
| heart disease treatment | cardiovascular care |
| heart disease treatment plan | heart health management plan |
| effective heart disease treatment | effective cardiac care |
| modern heart disease treatment | modern cardiovascular treatment |