Exercise Routines for All Ages: A Complete Guide to Staying Fit and Healthy
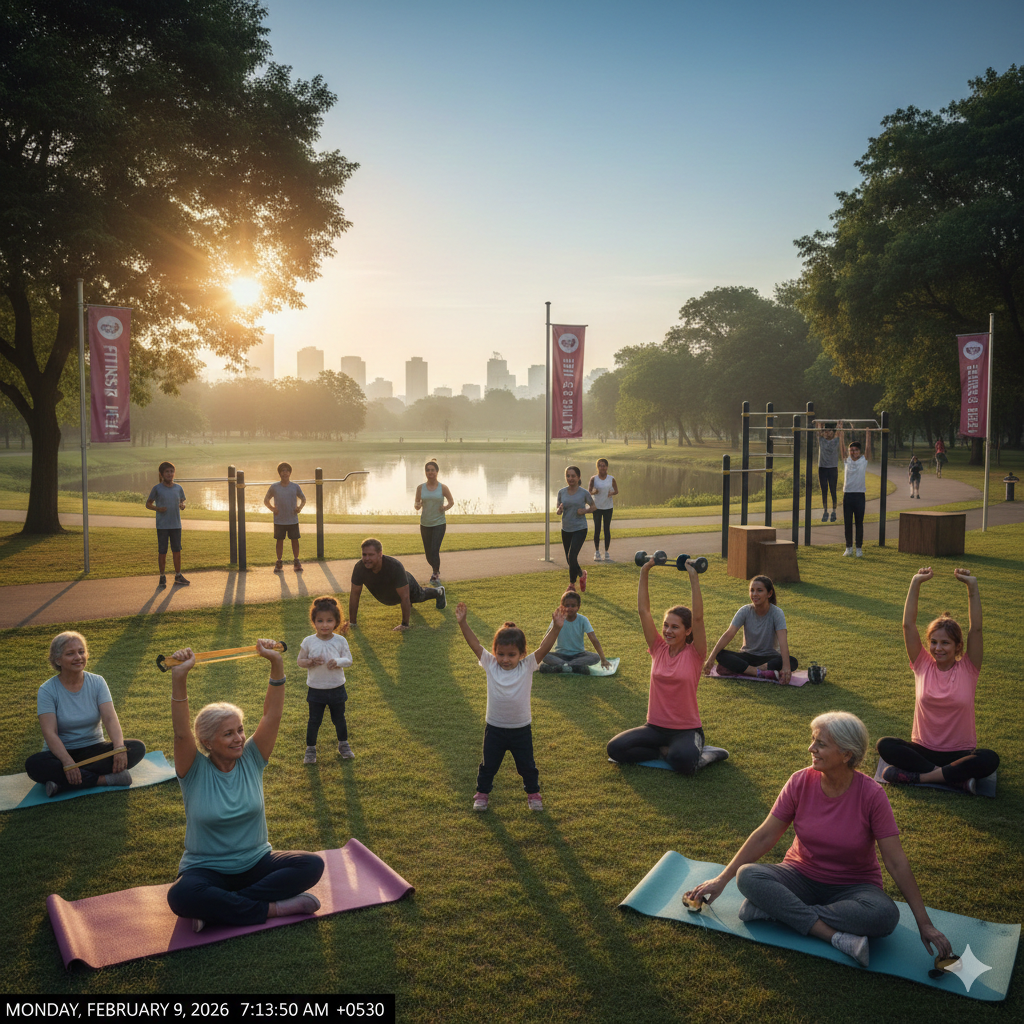
Exercise Routines for All Ages are essential for maintaining physical fitness, mental well-being, and overall health. Whether you are a child, teenager, adult, or senior, following age-appropriate exercise routines helps strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, boost cardiovascular health, and enhance mood. This comprehensive guide provides practical tips, workout examples, and safety advice for everyone, so you can stay active, healthy, and energized every day.
Table of Contents
- Benefits of Exercise at Every Age
- Exercise Guidelines for Children (5–12 Years)
- Exercise Guidelines for Teenagers (13–19 Years)
- Exercise Guidelines for Adults (20–64 Years)
- Exercise Guidelines for Seniors (65+ Years)
- Different Types of Exercises and Their Benefits
- Tips for Safe and Effective Workouts
- Creating Your Personalized Exercise Routine
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Motivation and Staying Consistent
- Conclusion
Benefits of Exercise at Every Age
Exercise has multi-dimensional benefits—physical, mental, and emotional. Regular activity can:
- Strengthen the heart and lungs: Aerobic exercise improves cardiovascular endurance.
- Build muscle and bone strength: Weight-bearing exercises increase bone density and prevent osteoporosis.
- Boost mental health: Exercise releases endorphins, reducing anxiety, depression, and stress.
- Improve flexibility and balance: Reduces risk of injuries and helps maintain independence.
- Promote social interaction: Group sports or exercise classes encourage teamwork and community.
- Manage weight: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy body weight.
Learn more about maintaining health through exercise at Health Guide Me – Fitness & Wellness.
Exercise Guidelines for Children (5–12 Years)
Children need physical activity to support growth, coordination, and motor skill development. Exercise should be enjoyable and varied.
Benefits for Children
- Develops strong bones and muscles.
- Improves motor skills and coordination.
- Reduces risk of childhood obesity.
- Encourages social skills and teamwork.
- Enhances focus and academic performance.
Recommended Activities
- Aerobic: Running, swimming, cycling, dancing, jumping rope.
- Strength: Bodyweight exercises like push-ups, squats, climbing, and playground activities.
- Flexibility: Stretching, yoga, or playful games that involve bending and twisting.
- Balance: Hopping on one foot, balance beams, or simple gymnastics exercises.
Sample Daily Routine for Children
| Time | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Light jogging or dynamic stretching | 5–10 min |
| Main activity | Running, swimming, or sports | 40–45 min |
| Strength & coordination | Bodyweight exercises, climbing, or games | 10–15 min |
| Cool-down | Stretching & slow walking | 5–10 min |
Tips:
- Keep activities playful to maintain interest.
- Encourage outdoor activities for exposure to sunlight and nature.
- Limit screen time to support physical activity.
Exercise Guidelines for Teenagers (13–19 Years)
Teenagers experience rapid growth, hormonal changes, and increased energy levels. Structured exercise supports physical development, athletic skills, and mental health.
Benefits for Teenagers
- Builds stronger bones and muscles.
- Improves cardiovascular fitness.
- Reduces stress and improves mental clarity.
- Encourages discipline and healthy habits for adulthood.
Recommended Activities
- Cardio: Running, swimming, cycling, basketball, soccer.
- Strength training: Supervised weightlifting, bodyweight exercises.
- Flexibility: Yoga, Pilates, or dynamic stretching.
- Coordination & agility: Dance, martial arts, or sports drills.
Sample Weekly Routine
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Cardio + strength | 60–90 min |
| Tuesday | Team sports or swimming | 60 min |
| Wednesday | Strength training | 60 min |
| Thursday | Cardio & flexibility | 60 min |
| Friday | Agility drills / sports | 60 min |
| Saturday | Outdoor recreational activity | 60–90 min |
| Sunday | Rest or light stretching | 20 min |
Safety Tips:
- Avoid lifting excessively heavy weights.
- Always warm up and stretch.
- Listen to your body to prevent injuries.
Exercise Guidelines for Adults (20–64 Years)
Adults need a balance of cardio, strength, and flexibility exercises to prevent lifestyle-related diseases, manage weight, and reduce stress.
Benefits for Adults
- Reduces risk of heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
- Maintains healthy weight and metabolism.
- Strengthens bones and muscles.
- Improves mental health and cognitive function.
- Enhances energy levels and quality of life.
Recommended Exercises
- Cardio: Brisk walking, running, swimming, cycling.
- Strength training: Resistance bands, bodyweight exercises, free weights.
- Flexibility: Yoga, Pilates, or regular stretching routines.
- Functional training: Exercises that mimic everyday movements like squats and lunges.
Sample Weekly Routine
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Cardio | 30 min |
| Tuesday | Strength training | 30–45 min |
| Wednesday | Yoga / Pilates | 30 min |
| Thursday | Cardio + functional exercises | 45 min |
| Friday | Strength training | 30–45 min |
| Saturday | Outdoor activity / sports | 30–60 min |
| Sunday | Rest or light stretching | 20 min |
Adults should aim for 150 minutes of moderate-intensity cardio per week and 2–3 strength training sessions.
Exercise Guidelines for Seniors (65+ Years)
Seniors should focus on gentle, low-impact exercises that improve balance, flexibility, and mobility. Maintaining physical activity helps prevent falls and chronic conditions.
Benefits for Seniors
- Improves cardiovascular health and muscle strength.
- Maintains joint flexibility.
- Reduces risk of falls and fractures.
- Boosts mood and cognitive function.
- Supports independence in daily life.
Recommended Activities
- Cardio: Walking, swimming, water aerobics.
- Strength: Light weights, resistance bands, chair exercises.
- Flexibility: Gentle yoga, stretching routines.
- Balance: Tai Chi, standing on one leg, balance exercises.
Sample Routine for Seniors
| Time | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Gentle walking or stretching | 5–10 min |
| Cardio | Walking or water aerobics | 10–20 min |
| Strength & balance | Resistance bands, squats, or chair exercises | 10–15 min |
| Cool-down | Stretching & relaxation | 5–10 min |
Safety Tips:
- Consult a doctor before starting new exercises.
- Avoid high-impact activities that stress joints.
- Use supportive footwear and maintain proper posture.
Different Types of Exercises and Their Benefits
- Aerobic Exercise (Cardio): Strengthens the heart and lungs, burns calories, and improves stamina.
- Strength Training: Builds muscles, strengthens bones, and enhances metabolism.
- Flexibility Exercises: Reduces stiffness, improves mobility, and prevents injuries.
- Balance Exercises: Improves coordination and reduces fall risk, especially for seniors.
- Functional Training: Mimics daily life activities, enhancing overall body function.
For more exercises, visit Health Guide Me – Fat Burn Exercises.
Tips for Safe and Effective Workouts
- Always warm up before and cool down after exercise.
- Use proper technique to prevent injuries.
- Stay hydrated.
- Wear suitable shoes and clothing.
- Gradually increase intensity over time.
- Rest adequately between workouts.
- Include variety to work all muscle groups and prevent boredom.
Creating Your Personalized Exercise Routine
- Set clear goals: Weight loss, strength, endurance, flexibility.
- Assess fitness level: Beginner, intermediate, advanced.
- Choose exercises: Mix cardio, strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Schedule workouts: Decide on frequency, duration, and type.
- Track progress: Use journals, apps, or wearable devices.
- Adjust as needed: Increase intensity or try new exercises to avoid plateaus.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping warm-ups and cool-downs
- Exercising with improper technique
- Overtraining without rest days
- Ignoring nutrition and hydration
- Not adjusting routines for age or ability
- Neglecting flexibility and balance exercises
Motivation and Staying Consistent
- Find a workout buddy for accountability.
- Set short-term and long-term goals.
- Reward yourself for milestones.
- Mix different types of exercise to keep things interesting.
- Track progress to stay motivated.
Staying consistent is more important than intensity. Even small, regular movements contribute to long-term health.
Conclusion
Exercise is a lifelong habit that provides countless physical, mental, and emotional benefits. Children should focus on playful activity and motor skills, teenagers on coordination and strength, adults on fitness and balance, and seniors on mobility, flexibility, and fall prevention. By following age-appropriate routines, maintaining consistency, and listening to your body, anyone can achieve a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Start today—every small step counts towards better health and longevity.
Exercise Routines for All Ages: A Complete and Detailed Guide
Exercise is essential for everyone, from children to seniors. Not only does it help maintain a healthy body, but it also boosts mental clarity, emotional stability, and overall quality of life. Each age group has specific needs, and following age-appropriate routines can maximize benefits while minimizing risks. This guide provides detailed routines, safety tips, and variations to suit all ages.
Why Exercise is Important for Every Age
Exercise is more than just physical activity. Its benefits include:
- Cardiovascular health: Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the heart and lungs.
- Muscle and bone strength: Weight-bearing exercises prevent osteoporosis and maintain muscle mass.
- Mental well-being: Exercise releases endorphins, reducing stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Flexibility and mobility: Stretching and balance exercises prevent falls and injuries.
- Weight management: Helps maintain a healthy body composition.
- Social engagement: Group classes and team sports promote social skills and community bonding.
For more on the benefits of physical activity, see Health Guide Me – Fitness & Wellness.

Exercise Guidelines for Children (5–12 Years)
Children should focus on fun, safe, and varied activities that help develop coordination, strength, and flexibility.
Benefits for Children
- Supports growth and development.
- Improves motor skills and agility.
- Reduces risk of childhood obesity.
- Promotes teamwork and social skills.
- Enhances focus, memory, and academic performance.
Recommended Activities
- Aerobic Activities: Running, swimming, cycling, skipping rope, dancing.
- Strength & Resistance: Bodyweight exercises (push-ups, squats), climbing, monkey bars.
- Flexibility: Stretching, playful yoga, obstacle courses.
- Balance: Hopping on one foot, balancing games, simple gymnastics exercises.
Daily Routine Example
| Time | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Light jogging, dynamic stretches | 5–10 min |
| Main Activity | Play, running, cycling, swimming | 30–40 min |
| Strength | Bodyweight exercises, climbing, games | 10–15 min |
| Cool-down | Stretching and slow walking | 5–10 min |
Indoor Options: Dancing, yoga for kids, indoor obstacle courses.
Outdoor Options: Playing tag, soccer, swimming, nature hikes.
Tips:
- Make it enjoyable to keep kids motivated.
- Mix indoor and outdoor activities.
- Encourage group play for social interaction.
Exercise Guidelines for Teenagers (13–19 Years)
Teenagers benefit from routines that build strength, stamina, and coordination while supporting growing bodies.
Benefits
- Enhances muscle and bone growth.
- Improves cardiovascular health.
- Reduces stress and promotes mental clarity.
- Encourages lifelong healthy habits.
Recommended Activities
- Cardio: Running, swimming, cycling, basketball, soccer.
- Strength Training: Supervised weight training, bodyweight exercises, resistance bands.
- Flexibility & Balance: Yoga, Pilates, martial arts.
- Agility & Coordination: Dance, team sports drills, ladder drills.
Sample Weekly Routine
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Cardio + strength | 60–90 min |
| Tuesday | Team sports | 60 min |
| Wednesday | Strength training | 60 min |
| Thursday | Cardio + yoga | 60 min |
| Friday | Agility drills / sports | 60 min |
| Saturday | Recreational outdoor activity | 60–90 min |
| Sunday | Rest / light stretching | 20 min |
Safety Tips:
- Avoid lifting excessive weights.
- Focus on proper form and technique.
- Include rest days to prevent overuse injuries.
Variations for Teens:
- Indoor: Jump rope, bodyweight circuit training, yoga.
- Outdoor: Hiking, swimming, cycling, sports leagues.
Exercise Guidelines for Adults (20–64 Years)
Adults need a balance of cardio, strength, flexibility, and functional training to stay healthy, maintain weight, and prevent lifestyle diseases.
Benefits
- Reduces risk of diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
- Supports bone and muscle health.
- Enhances mental health, focus, and energy.
- Promotes long-term mobility and independence.
Recommended Activities
- Cardio: Brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling.
- Strength Training: Weightlifting, resistance bands, bodyweight exercises.
- Flexibility & Mobility: Yoga, Pilates, dynamic stretching.
- Functional Training: Exercises that mimic daily life activities like squats, lunges, and lifting objects safely.
Sample Routine for Adults
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Cardio | 30–40 min |
| Tuesday | Strength training | 30–45 min |
| Wednesday | Yoga or Pilates | 30–40 min |
| Thursday | Cardio + functional training | 45 min |
| Friday | Strength training | 30–45 min |
| Saturday | Outdoor activity or sports | 45–60 min |
| Sunday | Rest or light stretching | 20 min |
Tips:
- Mix high-intensity and moderate-intensity sessions.
- Include both upper and lower body strength training.
- Track progress for motivation.
Variations:
- Indoor: Gym workouts, resistance bands, yoga classes.
- Outdoor: Walking, running, cycling, hiking.
Exercise Guidelines for Seniors (65+ Years)
For seniors, the focus should be on maintaining mobility, strength, balance, and cardiovascular health while preventing falls and injuries.
Benefits
- Improves strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Reduces risk of falls and injuries.
- Enhances cardiovascular health and stamina.
- Boosts mental health and cognitive function.
- Maintains independence in daily activities.
Recommended Activities
- Cardio: Walking, swimming, water aerobics, light cycling.
- Strength: Light weights, resistance bands, chair exercises.
- Flexibility: Gentle stretching, yoga, tai chi.
- Balance: Heel-to-toe walking, standing on one leg, balance board exercises.
Sample Routine
| Time | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Gentle walking / stretching | 5–10 min |
| Cardio | Walking or swimming | 10–20 min |
| Strength & balance | Light weights, chair exercises | 10–15 min |
| Cool-down | Stretching & relaxation | 5–10 min |
Indoor Options: Chair yoga, resistance bands, light dumbbell exercises.
Outdoor Options: Walking, tai chi in the park, swimming.
Safety Tips:
- Consult a doctor before starting new exercises.
- Avoid high-impact or risky exercises.
- Wear supportive shoes and maintain proper posture.
Types of Exercises for All Ages
- Aerobic Exercise (Cardio): Boosts heart and lung health.
- Examples: Walking, running, swimming, cycling, dancing.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle, supports bone health, improves metabolism.
- Examples: Bodyweight exercises, dumbbells, resistance bands.
- Flexibility & Mobility: Enhances range of motion and prevents injuries.
- Examples: Yoga, Pilates, stretching routines.
- Balance & Coordination: Reduces fall risk and improves posture.
- Examples: Tai Chi, balance board exercises, single-leg stance.
- Functional Training: Mimics real-life movements to enhance daily performance.
- Examples: Squats, lunges, step-ups, lifting objects safely.
More exercise examples can be found at Health Guide Me – Fat Burn & Exercises.
Tips for Safe and Effective Workouts
- Always warm up before exercising and cool down afterward.
- Focus on proper form to prevent injuries.
- Stay hydrated before, during, and after workouts.
- Wear suitable shoes and clothing.
- Gradually increase intensity and duration.
- Include rest days for recovery.
- Maintain variety to work all muscle groups.
Creating a Personalized Exercise Routine
- Define goals: Weight loss, strength, endurance, flexibility, or overall health.
- Assess fitness level: Beginner, intermediate, or advanced.
- Select exercises: Include cardio, strength, flexibility, and balance.
- Plan frequency and duration: Based on availability and goals.
- Track progress: Use apps, journals, or wearable devices.
- Adjust as needed: Increase intensity or change exercises to avoid plateaus.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Skipping warm-ups or cool-downs
- Ignoring proper technique
- Exercising through pain
- Overtraining without rest
- Neglecting nutrition and hydration
- Not adjusting exercises for age or ability
- Focusing only on one type of exercise (e.g., only cardio or strength)
Motivation and Consistency
- Find a workout buddy or join a class.
- Set realistic short-term and long-term goals.
- Reward milestones with small incentives.
- Mix different exercises to avoid boredom.
- Track progress visually or digitally.
Remember, consistency is more important than intensity. Even small daily movements add up over time.
Conclusion
Exercise is vital for maintaining health, fitness, and overall well-being at every stage of life. By following age-appropriate routines, mixing types of exercises, and listening to your body, anyone can achieve long-term health benefits. Children should focus on playful activity, teenagers on strength and coordination, adults on fitness and balance, and seniors on mobility and fall prevention. Start today—every step, stretch, or rep counts toward a healthier, happier life.
Best Exercise Routines for All Ages to Stay Fit and Healthy
Exercise Routines for All Ages are essential for maintaining physical fitness, improving strength, and boosting mental well-being. No matter your age — whether you are a child, teenager, adult, or senior — following age-appropriate exercise routines can help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, enhance cardiovascular health, and support mental health.
For more expert health and fitness guidance, visit Health Guide Me.
1. Why Exercise Is Important for All Ages
Exercise is not just about staying in shape — it affects nearly every aspect of your health:
- Improves cardiovascular health: Aerobic exercises like jogging, swimming, or cycling strengthen your heart and lungs.
- Builds strength and flexibility: Bodyweight exercises, resistance bands, and stretching prevent injuries and improve mobility.
- Boosts mental health: Physical activity releases endorphins that reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Supports immunity: Regular exercise strengthens your immune system. Learn more about immune health at HIV & Immune System.
- Helps maintain a healthy weight: Combining cardio and strength exercises supports metabolism and fat loss.
For detailed guidance on recommended physical activity levels, see the CDC Physical Activity Guidelines.
2. Exercise Guidelines for Children (5–12 Years)
Children require activities that are fun, varied, and safe. These activities help develop motor skills, coordination, and strength.
Recommended Exercises:
- Cardio: Running, swimming, cycling, skipping rope
- Strength: Bodyweight exercises, climbing, playful obstacle courses
- Flexibility: Stretching routines or kids’ yoga
- Balance: Hopping games, gymnastics basics, balance exercises
Sample Daily Routine:
| Time | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Light jogging & stretching | 5–10 min |
| Main Activity | Running, cycling, outdoor play | 30–40 min |
| Strength | Bodyweight exercises & climbing | 10–15 min |
| Cool-down | Stretching & slow walking | 5–10 min |
Tip: Mix indoor and outdoor activities to keep children motivated and active.
3. Exercise Guidelines for Teenagers (13–19 Years)
Teenagers should focus on strength, endurance, flexibility, and coordination. Proper exercise at this age helps prevent injuries, improves posture, and boosts mental focus.
Recommended Activities:
- Cardio: Running, swimming, cycling, team sports
- Strength Training: Supervised weightlifting or resistance bands
- Flexibility: Yoga, Pilates, martial arts
- Agility & Balance: Ladder drills, dance, sports-specific drills
Weekly Routine Example:
- Monday: Cardio + strength (60–90 min)
- Tuesday: Team sports (60 min)
- Wednesday: Strength training (60 min)
- Thursday: Cardio + yoga (60 min)
- Friday: Agility drills or sports (60 min)
- Saturday: Recreational outdoor activity (60–90 min)
- Sunday: Rest / light stretching (20 min)
Tip: Avoid overtraining and focus on proper form to prevent injuries.
4. Exercise Guidelines for Adults (20–64 Years)
Adults should combine cardio, strength, flexibility, and functional exercises for overall fitness. These exercises help maintain energy levels, prevent chronic diseases, and improve mental well-being.
Recommended Exercises:
- Cardio: Brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling
- Strength: Weightlifting, resistance bands, bodyweight exercises
- Flexibility: Yoga, Pilates, stretching
- Functional: Squats, lunges, lifting objects safely
For workouts specifically aimed at fat loss, check Fat Burn Exercises and Foods.
Sample Weekly Routine:
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Cardio | 30–40 min |
| Tuesday | Strength Training | 30–45 min |
| Wednesday | Yoga / Pilates | 30–40 min |
| Thursday | Cardio + Functional | 45 min |
| Friday | Strength Training | 30–45 min |
| Saturday | Outdoor activity / sports | 45–60 min |
| Sunday | Rest / light stretching | 20 min |
5. Exercise Guidelines for Seniors (65+ Years)
Seniors should focus on low-impact exercises that improve balance, mobility, and overall health while reducing the risk of falls.
Recommended Exercises:
- Cardio: Walking, swimming, water aerobics
- Strength: Light weights, resistance bands, chair exercises
- Flexibility: Gentle yoga, stretching, Tai Chi
- Balance: Heel-to-toe walking, single-leg standing
Sample Routine:
| Time | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Warm-up | Gentle walking & stretching | 5–10 min |
| Cardio | Walking / swimming | 10–20 min |
| Strength & Balance | Resistance bands / chair exercises | 10–15 min |
| Cool-down | Stretching & relaxation | 5–10 min |
Tip: Always consult a doctor before starting a new exercise routine.
6. Types of Exercises
- Cardio (Aerobic): Boosts heart and lung health
- Strength Training: Builds muscles, supports bones
- Flexibility & Mobility: Reduces stiffness, improves range of motion
- Balance Exercises: Prevent falls and improve coordination
- Functional Training: Prepares the body for daily movements
7. Safety Tips for All Ages
- Warm up and cool down properly
- Maintain proper form and posture
- Stay hydrated during workouts
- Wear appropriate shoes and clothing
- Gradually increase intensity
- Include rest days in your schedule
- Combine different exercise types for best results
8. Staying Motivated
- Exercise with a buddy or join group classes
- Set realistic short-term and long-term goals
- Reward yourself for milestones achieved
- Mix different exercises to prevent boredom
- Track your progress visually or with apps
Consistency is more important than intensity — even small daily activities can contribute to long-term health.







