Diabetes: Causes, Types, Symptoms, Prevention, and Management (Complete Guide for US, UK & Canada)
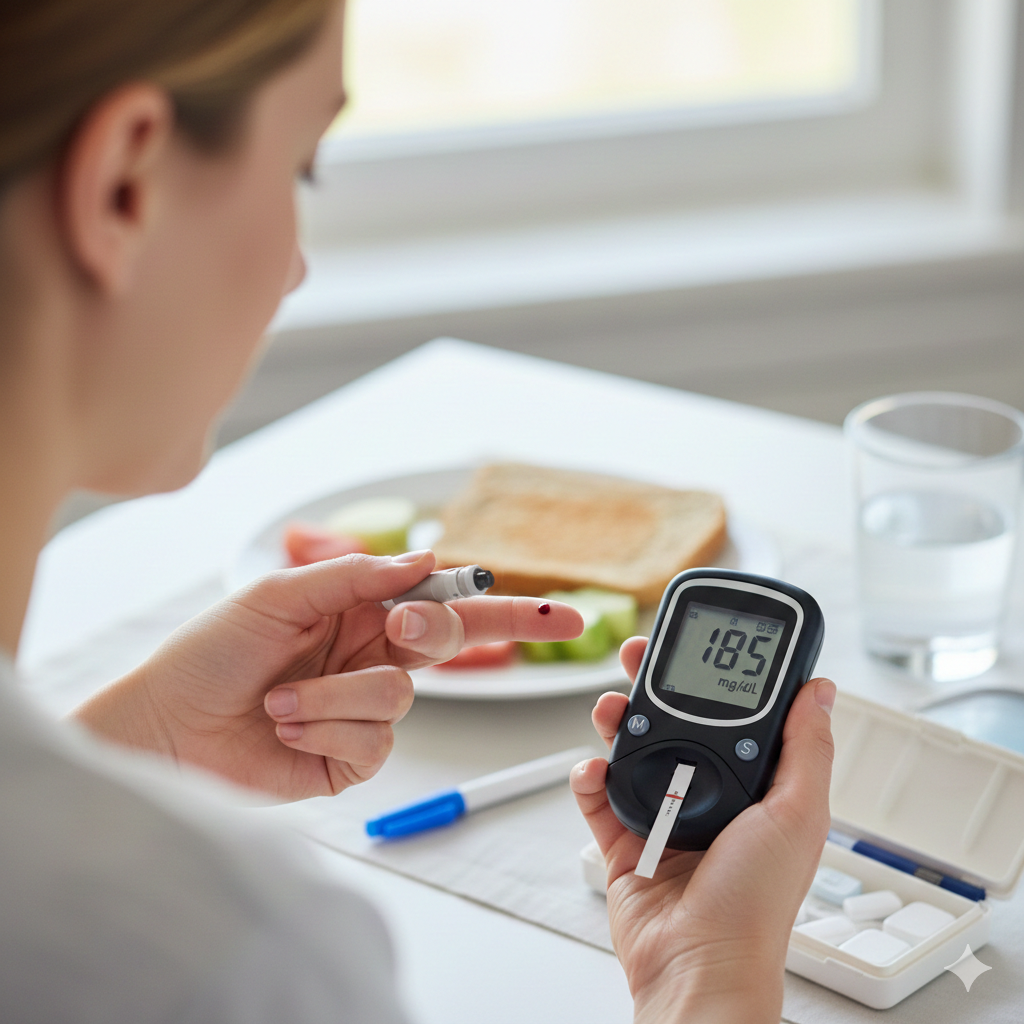

Introduction to Diabetes
Diabetes is one of the most common chronic health conditions affecting millions of people worldwide, particularly in the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada. It is a long-term metabolic disease characterized by high blood sugar (glucose) levels that can lead to serious health complications if not properly managed.
According to public health data, diabetes prevalence continues to rise due to unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, obesity, aging populations, and genetic factors. Understanding diabetes—its causes, symptoms, types, prevention strategies, and treatment options—is essential for individuals, families, healthcare professionals, and policymakers.
This comprehensive article provides a complete, SEO-optimized guide to diabetes, designed to meet the information needs of readers in North America and the UK, while following best practices for health content.
What Is Diabetes?
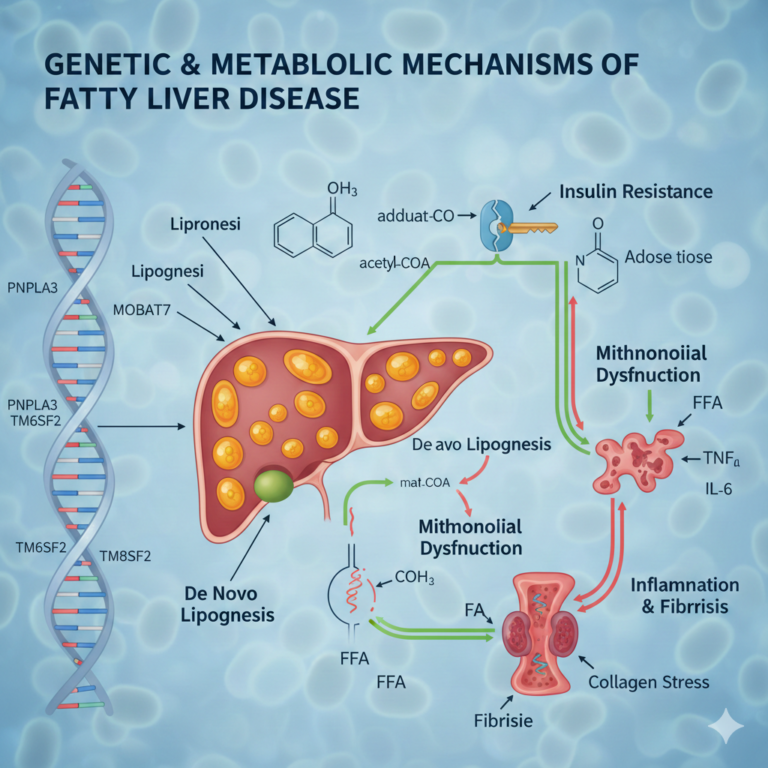
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic medical condition that occurs when the body cannot properly regulate blood glucose levels. Glucose is the body’s main source of energy and comes from the food we eat. Insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, helps glucose enter cells where it is used for energy.
Diabetes develops when:
- The body does not produce enough insulin
- The body cannot use insulin effectively
- Or both
As a result, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
Types of Diabetes
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition in which the immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
Key characteristics:
- Usually diagnosed in children, teenagers, or young adults
- Not caused by lifestyle factors
- Requires lifelong insulin therapy
- Accounts for approximately 5–10% of diabetes cases
Common symptoms:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- Sudden weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Blurred vision
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, especially in the US, UK, and Canada.
Key characteristics:
- Body becomes resistant to insulin
- Strongly linked to obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet
- Often develops gradually
- Can be managed with lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes insulin
Risk factors include:
- Being overweight or obese
- Family history of diabetes
- Age over 35–40
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Gestational diabetes history
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually disappears after childbirth.
Important facts:
- Increases risk of Type 2 diabetes later in life
- Can affect baby’s birth weight and future health
- Common in pregnant women in North America and the UK
4. Prediabetes
Prediabetes is a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes.
Why it matters:
- Strong warning sign
- Lifestyle changes can prevent or delay Type 2 diabetes
- Very common in adults in the US, UK, and Canada
Causes of Diabetes
Biological Causes
- Insulin resistance
- Autoimmune destruction of beta cells
- Hormonal imbalances
Lifestyle Factors
- Poor diet (high sugar, refined carbs)
- Lack of physical activity
- Obesity
- Chronic stress
- Sleep deprivation
Genetic Factors
- Family history of diabetes
- Ethnic background (higher risk in South Asian, African, Indigenous populations)
Symptoms of Diabetes
Common diabetes symptoms include:
- Increased thirst (polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (polyuria)
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Frequent infections
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
⚠️ Many people with Type 2 diabetes may have no symptoms for years, making early screening crucial.
Diagnosis of Diabetes
Healthcare providers in the US, UK, and Canada commonly use the following tests:
Blood Tests
- Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG)
- HbA1c (A1C test) – gold standard
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
- Random Blood Sugar Test
Diagnostic Criteria (General)
- A1C ≥ 6.5%
- Fasting glucose ≥ 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L)
Diabetes Treatment and Management
1. Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle management is the foundation of diabetes care.
Healthy Diet
- Whole grains
- Lean protein
- Fruits and vegetables
- Healthy fats
- Low sugar intake
Popular diet approaches:
- Mediterranean diet
- DASH diet
- Low-glycemic index diet
- Plant-based diets
2. Physical Activity
Regular exercise:
- Improves insulin sensitivity
- Helps control weight
- Reduces cardiovascular risk
Recommended activities:
- Walking
- Cycling
- Swimming
- Strength training
3. Medications
Common diabetes medications include:
- Metformin
- Sulfonylureas
- GLP-1 receptor agonists
- SGLT2 inhibitors
- Insulin therapy
Medication choice depends on:
- Type of diabetes
- Age
- Other medical conditions
- Healthcare guidelines (NHS, CDC, Health Canada)
4. Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Finger-stick glucose testing
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)
- Smart health apps and wearables

Diabetes Complications
Poorly controlled diabetes can lead to serious complications:
Short-Term Complications
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyperglycemia
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
Long-Term Complications
- Heart disease and stroke
- Kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy)
- Eye damage (diabetic retinopathy)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Foot ulcers and amputations
Diabetes Prevention
Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
Evidence from the US, UK, and Canada shows that Type 2 diabetes is largely preventable.
Key prevention strategies:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
- Quit smoking
- Manage stress
- Get regular health screenings
Diabetes in the United States
- Over 37 million Americans live with diabetes
- Leading cause of heart disease and kidney failure
- Major public health focus by CDC and NIH
- High healthcare costs and economic burden
Diabetes in the United Kingdom
- Over 5 million people affected
- Managed through the NHS
- Strong focus on prevention programs
- National Diabetes Audit tracks outcomes
Diabetes in Canada
- Over 3.7 million Canadians diagnosed
- Indigenous populations face higher risk
- Managed through provincial healthcare systems
- Strong emphasis on community health programs
Mental Health and Diabetes
Diabetes is closely linked to mental health conditions such as:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Diabetes distress
- Burnout
Integrated care models in US, UK, and Canada emphasize mental health support as part of diabetes management.
Technology and Innovation in Diabetes Care
Modern diabetes management includes:
- Artificial pancreas systems
- AI-powered glucose prediction
- Telemedicine
- Mobile health apps
- Wearable glucose monitors
These technologies are rapidly expanding across North America and Europe.
Living Well With Diabetes
Living with diabetes requires:
- Education
- Self-management skills
- Support from healthcare providers
- Family and community involvement
With proper care, people with diabetes can live long, healthy, and active lives.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a serious but manageable chronic condition that affects millions in the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada. Early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, proper medical care, and ongoing education are essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
By increasing awareness and adopting healthier lifestyles, individuals and societies can significantly reduce the impact of diabetes.
Diabetes and Cardiovascular Health
Diabetes is strongly associated with cardiovascular diseases, which remain the leading cause of death among people with diabetes in the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada. High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart, significantly increasing the risk of serious heart-related conditions.
Common Cardiovascular Complications
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease
- High blood pressure
People with diabetes are two to four times more likely to develop heart disease compared to those without diabetes. Managing blood sugar, cholesterol levels, and blood pressure is critical for reducing cardiovascular risk.
Diabetes and Kidney Disease (Diabetic Nephropathy)
Diabetes is the leading cause of chronic kidney disease in North America and the UK. Prolonged high blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in the kidneys, reducing their ability to filter waste from the blood.
Warning Signs
- Swelling in feet and ankles
- Fatigue
- Changes in urination
- High blood pressure
- Protein in urine
Early detection through regular kidney function tests can slow or prevent progression to kidney failure.
Diabetes and Eye Health
Diabetic eye disease is a major cause of preventable blindness.
Major Eye Conditions
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Diabetic macular edema
- Glaucoma
- Cataracts
Annual eye examinations are recommended by healthcare authorities such as the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the UK NHS.
Diabetes and Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Diabetic neuropathy affects millions of individuals and often develops after years of uncontrolled diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy
- Tingling or burning sensations
- Numbness in hands and feet
- Muscle weakness
- Digestive problems
- Sexual dysfunction
Good glucose control is the most effective way to prevent nerve damage.
Diabetes and Foot Care
Foot complications are common due to nerve damage and poor circulation.
Foot Care Best Practices
- Daily foot inspection
- Proper footwear
- Immediate treatment of cuts or blisters
- Regular podiatrist visits
Preventive foot care significantly reduces the risk of amputations.
Diabetes in Children and Adolescents
Although Type 1 diabetes is more common in children, Type 2 diabetes is increasingly diagnosed in youth, particularly in the US and Canada.
Contributing Factors
- Childhood obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- High-sugar diets
- Family history
Early intervention is essential to prevent lifelong complications.
Diabetes and Pregnancy
Diabetes during pregnancy requires special medical attention.
Risks of Poor Control
- Pre-eclampsia
- Premature birth
- Large birth weight babies
- Birth complications
With proper prenatal care, most women with diabetes can have healthy pregnancies.
Diabetes and Aging Population
As populations age in the US, UK, and Canada, diabetes prevalence among older adults continues to rise.
Challenges in Older Adults
- Multiple chronic conditions
- Risk of hypoglycemia
- Cognitive decline
- Medication management
Personalized treatment plans are essential for elderly patients.
Diabetes and Ethnic Disparities
Certain ethnic groups face a higher risk of diabetes due to genetic, socioeconomic, and environmental factors.
High-Risk Populations
- South Asian communities
- African and Caribbean populations
- Indigenous peoples
- Hispanic and Latino populations
Public health programs increasingly focus on culturally tailored prevention strategies.
Role of Education in Diabetes Management
Diabetes education programs empower individuals to manage their condition effectively.
Diabetes Self-Management Education (DSME)
- Nutrition education
- Medication adherence
- Blood glucose monitoring
- Stress management
Studies show that individuals who participate in structured education programs have better outcomes.
Role of Primary Care and Healthcare Systems
Healthcare systems in the US, UK, and Canada emphasize integrated care models.
Key Components
- Regular screenings
- Multidisciplinary care teams
- Digital health solutions
- Community-based programs
Strong primary care access improves early diagnosis and long-term outcomes.
Public Health Policies and Diabetes Prevention
Governments are implementing policies aimed at reducing diabetes prevalence.
Examples
- Sugar taxes
- Food labeling regulations
- Public awareness campaigns
- School nutrition programs
- Workplace wellness initiatives
These policies play a crucial role in population-level prevention.
Economic Impact of Diabetes
Diabetes places a heavy economic burden on healthcare systems.
Estimated Costs
- Billions in direct medical costs
- Lost productivity
- Disability-related expenses
Preventive care and early intervention are cost-effective strategies.
Diabetes Research and Future Treatments
Ongoing research offers hope for improved treatments and potential cures.
Emerging Areas of Research
- Stem cell therapy
- Beta-cell regeneration
- Artificial pancreas systems
- Gene therapy
- Personalized medicine
Research institutions in the US, UK, and Canada are at the forefront of diabetes innovation.
Myths and Misconceptions About Diabetes
Common Myths
- Diabetes is caused only by sugar
- People with diabetes cannot eat carbohydrates
- Insulin means failure
- Diabetes is not a serious disease
Accurate information is essential to reduce stigma and improve care.
Lifestyle Tips for Long-Term Diabetes Control
Daily Habits That Matter
- Consistent meal timing
- Adequate sleep
- Stress reduction techniques
- Smoking cessation
- Alcohol moderation
Small, consistent changes can lead to significant improvements.
Diabetes and Quality of Life
With proper management, individuals with diabetes can:
- Maintain full-time employment
- Travel safely
- Participate in sports
- Live independently
- Enjoy a high quality of life
Support systems and education play a critical role.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetes (SEO Boost)
Is diabetes curable?
Currently, there is no cure, but diabetes can be effectively managed.
Can diabetes be reversed?
Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be put into remission through weight loss and lifestyle changes.
Is diabetes hereditary?
Genetics play a significant role, especially in Type 2 diabetes.
How often should blood sugar be checked?
Frequency depends on diabetes type and treatment plan.
Final Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex, lifelong condition that affects millions of people across the United States, United Kingdom, and Canada. While it poses serious health risks, modern medical advances, lifestyle interventions, and public health initiatives have made it possible for individuals with diabetes to live long, productive, and fulfilling lives.
Early detection, continuous education, proper treatment, and supportive healthcare systems remain the cornerstones of effective diabetes management. By addressing lifestyle factors and reducing health inequalities, societies can significantly reduce the global burden of diabetes.
SEO Keyword Expansion (Extra Boost)
- Diabetes causes
- Diabetes signs and symptoms
- Diabetes diet plan
- Diabetes medications
- Blood glucose control
- Insulin therapy
- Diabetes complications prevention
- Diabetes healthcare systems
- Diabetes lifestyle management
- Chronic disease management
High-Value SEO Keywords Used (US / UK / Canada)
- Diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Diabetes symptoms
- Diabetes treatment
- Diabetes prevention
- Blood sugar levels
- Insulin resistance
- Diabetes management
- Diabetes complications
- Diabetes in the US
- Diabetes in the UK
- Diabetes in Canada
- Gestational diabetes
- Prediabetes
Trusted Health Information for Chronic Disease Management
Managing chronic conditions such as diabetes requires access to reliable and evidence-based health information. At Health Guide Me (https://healthguideme.com/), readers can explore in-depth guides on diabetes, heart health, blood pressure, and cholesterol management. These resources are designed to help individuals make informed lifestyle and medical decisions for long-term health improvement.
The Connection Between Diabetes and High Blood Pressure
Diabetes and high blood pressure often occur together and significantly increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. Poor blood sugar control can damage blood vessels, making blood pressure more difficult to manage over time. Understanding how these conditions are linked is essential for reducing cardiovascular complications and improving overall health outcomes.
For more detailed information, read our complete blood pressure management guide here:
https://healthguideme.com/blood-pressure-guide/
Why Cholesterol Control Is Critical for People With Diabetes
People living with diabetes are more likely to develop unhealthy cholesterol levels, including high LDL (bad cholesterol) and low HDL (good cholesterol). This combination greatly increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. Managing cholesterol through diet, physical activity, and proper medical care is a key part of comprehensive diabetes management.
To learn more, visit our cholesterol health complete guide:
https://healthguideme.com/cholesterol-health-complete-guide/
Reliable External Health Resources on Diabetes
For accurate and up-to-date medical information, it is important to rely on trusted global and national health organizations. These institutions provide evidence-based guidance on diabetes prevention, diagnosis, and management.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), diabetes is a major public health concern in the United States, affecting millions of adults and increasing the risk of heart disease, kidney failure, and vision loss. You can explore official diabetes information and statistics here:
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes
Diabetes Care Guidelines in the United Kingdom
In the United Kingdom, diabetes care and treatment guidelines are provided by the National Health Service (NHS). The NHS emphasizes early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and long-term management to reduce diabetes-related complications.
For NHS-approved information on diabetes symptoms, treatment options, and patient care, visit:
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/diabetes/
Global Perspective on Diabetes and Public Health
The World Health Organization (WHO) highlights diabetes as one of the fastest-growing global health challenges. WHO focuses on prevention strategies, access to essential medicines, and reducing health inequalities related to diabetes worldwide.
To learn more about diabetes from a global public health perspective, see:
https://www.who.int/health-topics/diabetes
Diabetes Information and Research in Canada
In Canada, diabetes prevention and management are supported by national public health programs. Health Canada provides education, research, and community-based initiatives to help reduce the burden of diabetes across the country.
Official diabetes resources from Health Canada are available at:
https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/chronic-diseases/diabetes.html
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition that affects how the body regulates blood sugar levels. This condition develops when insulin production is insufficient or when the body cannot use insulin effectively. Poor blood sugar control increases the risk of heart disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage.
this chronic condition
this metabolic disorder
the condition
high blood sugar disorder
long-term metabolic condition
blood sugar imbalance
glucose regulation disorder
the disease
this health condition
| Condition | mg/dL (US / Canada) | mmol/L (UK / International) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 100 | Less than 5.6 |
| Prediabetes | 100 – 125 | 5.6 – 6.9 |
| Diabetes | 126 or higher | 7.0 or higher |
| Condition | mg/dL | mmol/L |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Less than 140 | Less than 7.8 |
| Prediabetes | 140 – 199 | 7.8 – 11.0 |
| Diabetes | 200 or higher | 11.1 or higher |