Cholesterol Health: The Ultimate Complete Guide to Understanding, Managing, and Improving Your Cholesterol Naturally and Medically
Introduction
Cholesterol is one of the most misunderstood substances in human health. For decades, it has been blamed as the primary cause of heart disease, yet modern science has revealed a far more complex and nuanced story. Cholesterol is not inherently bad; in fact, it is essential for life. Every cell in your body depends on cholesterol to function properly. Problems arise only when cholesterol levels become imbalanced or when certain types of cholesterol dominate others.
This comprehensive guide explains cholesterol in complete detail: what it is, why your body needs it, different types of cholesterol, causes of high cholesterol, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, diet plans, lifestyle changes, medications, myths, and long-term prevention strategies. This article is written in simple but professional English and is designed to serve as a full reference for patients, students, and health-conscious individuals.
Cholesterol Health is a critical part of overall wellbeing, as balanced cholesterol levels play a major role in protecting the heart, brain, and blood vessels from serious diseases.
Cholesterol Health: The Ultimate Complete Guide

What Is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in all cells of the body. It belongs to a group of molecules called lipids. Although cholesterol often gets a negative reputation, it plays several vital roles in maintaining health.
Your body produces cholesterol naturally, mainly in the liver. Additionally, cholesterol enters the body through certain foods, especially animal-based foods such as meat, eggs, dairy products, and seafood.
Key Functions of Cholesterol
- Helps build and maintain cell membranes
- Essential for the production of steroid hormones such as estrogen, testosterone, and cortisol
- Required for the synthesis of vitamin D
- Necessary for producing bile acids, which help digest fats
- Supports proper brain and nerve function
Without cholesterol, the human body cannot survive.
Types of Cholesterol
Cholesterol travels through the bloodstream attached to proteins. These combinations are called lipoproteins. There are several types of lipoproteins, but the most important ones are:
1. Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) – “Bad Cholesterol”
LDL cholesterol carries cholesterol from the liver to the cells. When there is too much LDL in the blood, it can deposit cholesterol on the walls of arteries. Over time, this buildup forms plaques, leading to narrowed or blocked arteries.
High LDL cholesterol is strongly associated with:
- Atherosclerosis
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Peripheral artery disease
2. High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) – “Good Cholesterol”
HDL cholesterol helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transports it back to the liver for elimination. Higher HDL levels are protective against heart disease.
Benefits of HDL cholesterol:
- Reduces plaque buildup
- Lowers risk of cardiovascular disease
- Supports overall heart health
3. Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL)
VLDL mainly carries triglycerides rather than cholesterol. High VLDL levels contribute to plaque formation and are linked with metabolic disorders.
4. Triglycerides
Triglycerides are not cholesterol but are closely related. They are the most common type of fat in the body and store excess energy from food. High triglyceride levels increase the risk of heart disease, especially when combined with high LDL or low HDL.
Normal Cholesterol Levels
According to international health guidelines, the recommended cholesterol levels for adults are:
- Total Cholesterol: Below 200 mg/dL
- LDL Cholesterol: Below 100 mg/dL (below 70 mg/dL for high-risk individuals)
- HDL Cholesterol: Above 40 mg/dL (men), above 50 mg/dL (women)
- Triglycerides: Below 150 mg/dL
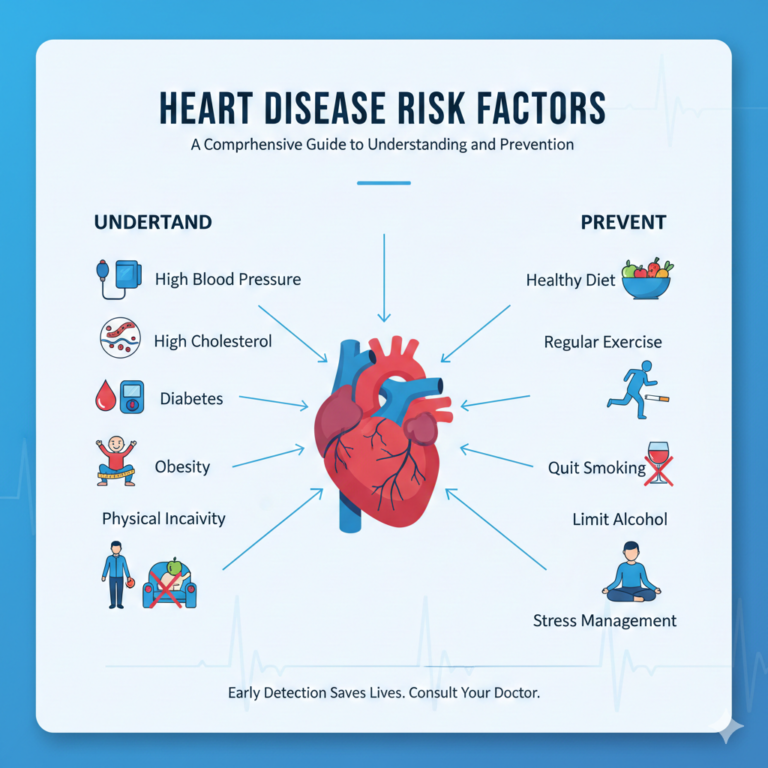
Causes of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol, also known as hypercholesterolemia, develops due to a combination of lifestyle, genetic, and medical factors.
Dietary Causes
- High intake of saturated fats
- Consumption of trans fats
- Excessive fried and processed foods
- High sugar and refined carbohydrate intake
Lifestyle Factors
- Physical inactivity
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
Medical Conditions
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypothyroidism
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Genetic Factors
Some individuals inherit genes that cause the body to produce too much cholesterol or remove too little from the blood. This condition is called familial hypercholesterolemia.
Symptoms of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol usually does not cause noticeable symptoms. This is why it is often referred to as a “silent condition.” Many people only discover they have high cholesterol after a heart attack or stroke.
However, in severe or genetic cases, symptoms may include:
- Yellowish deposits around the eyes (xanthelasma)
- Fatty lumps under the skin (xanthomas)
- Chest pain (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
Health Risks of High Cholesterol
If left untreated, high cholesterol can lead to serious and life-threatening conditions.
Cardiovascular Diseases
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Heart failure
Other Complications
- Peripheral artery disease
- Erectile dysfunction
- Chronic kidney disease
- Cognitive decline
Cholesterol and Heart Disease
High LDL cholesterol damages the inner lining of arteries, allowing cholesterol to enter the artery wall. Over time, plaques harden and narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow. A plaque rupture can cause a blood clot, leading to a heart attack or stroke.
Diagnosis: Cholesterol Blood Tests
Cholesterol is measured using a lipid profile test.
Types of Tests
- Total cholesterol
- LDL cholesterol
- HDL cholesterol
- Triglycerides
The test is usually done after fasting for 9–12 hours.
Treatment Options for High Cholesterol
Treatment depends on cholesterol levels, age, overall health, and cardiovascular risk.
Lifestyle Modification (First-Line Treatment)
Lifestyle changes are the foundation of cholesterol management.
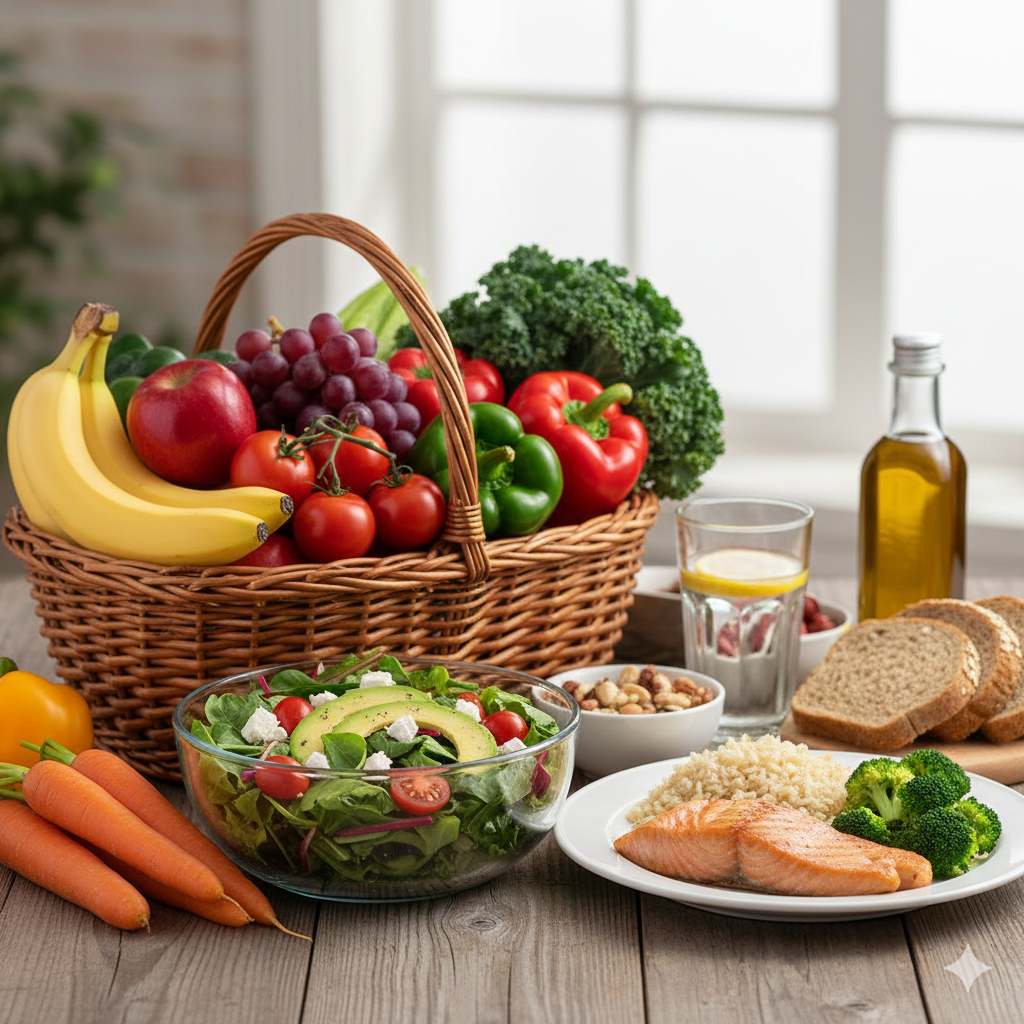

Diet for Healthy Cholesterol Levels
Foods to Eat
- Whole grains (oats, brown rice, barley)
- Fruits (apples, berries, citrus fruits)
- Vegetables (leafy greens, broccoli, carrots)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, beans)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds)
- Healthy fats (olive oil, avocado)
Foods to Avoid
- Fried foods
- Processed meats
- Full-fat dairy products
- Sugary snacks and drinks
- Bakery products with trans fats
Vegetarian and Plant-Based Cholesterol Management
A well-planned vegetarian diet can significantly reduce LDL cholesterol. Plant sterols, soluble fiber, and antioxidants play key roles in cholesterol reduction.
Physical Activity and Cholesterol
Regular exercise improves cholesterol levels by:
- Increasing HDL cholesterol
- Reducing LDL cholesterol
- Lowering triglycerides
Recommended activities include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and strength training.
Weight Management
Losing even 5–10% of body weight can significantly reduce cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Smoking and Alcohol
Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol and damages blood vessels. Quitting smoking rapidly improves cholesterol balance. Moderate alcohol intake may raise HDL, but excess intake raises triglycerides.
Medications for High Cholesterol
Statins
- Atorvastatin
- Rosuvastatin
- Simvastatin
Statins reduce LDL cholesterol and lower heart attack risk.
Other Medications
- Ezetimibe
- PCSK9 inhibitors
- Fibrates
- Bile acid sequestrants
Natural Supplements for Cholesterol
- Plant sterols
- Psyllium husk
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Red yeast rice (medical supervision required)
Cholesterol Myths and Facts
Myth: All cholesterol is bad
Fact: Cholesterol is essential for life.
Myth: Only overweight people have high cholesterol
Fact: Genetics play a major role.
Cholesterol in Different Age Groups
Children and Adolescents
Early screening is important for high-risk families.
Adults
Regular monitoring is essential after age 20.
Elderly
Balanced treatment is required to avoid side effects.
Long-Term Prevention Strategies
- Healthy diet
- Regular exercise
- Routine blood tests
- Stress management
- Adequate sleep
Future Research and Advances
New therapies and personalized medicine approaches are improving cholesterol management.
Conclusion
Cholesterol management is a lifelong commitment. Understanding cholesterol empowers individuals to make informed decisions, prevent heart disease, and live longer, healthier lives. With the right balance of diet, lifestyle changes, and medical care, cholesterol can be effectively controlled.
This guide is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice.
| Component | Role | 2026 Target Range |
| LDL (Bad) | Delivers cholesterol to cells; can clog arteries. | < 100 mg/dL (ideal); < 70 (high risk) |
| HDL (Good) | Acts as a “scavenger,” taking cholesterol to the liver. | > 40 mg/dL (men); > 50 (women) |
| Triglycerides | Store excess energy from your diet as fat. | < 150 mg/dL |
| Total Cholesterol | The sum of your HDL, LDL, and 20% of triglycerides. | < 200 mg/dL |
Maintaining Cholesterol Health requires accurate, reliable information from both expert external sources and detailed internal guidance. For medically verified recommendations, you can refer to trusted global health organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) – https://www.who.int, the American Heart Association (AHA) – https://www.heart.org, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – https://www.cdc.gov. These external resources provide guidance on managing LDL and HDL cholesterol, preventing heart disease, and understanding risk factors.
Along with these external references, it is important to explore internal resources on our website to strengthen your knowledge. For example, the Heart Health Guide (https://healthguideme.com/prioritizing-your-gut-a-guide-to-digestive-health-guide-to-digestive-health-and-microbiome/) explains how cholesterol impacts the heart and blood vessels, the Healthy Diet Plan (hthttps://healthguideme.com/digestive-health-complete-guide/ps://yourwebsite.com/healthy-diet-plan/) provides practical tips to reduce LDL and boost HDL naturally, and the High Blood Pressure Guidehttps://healthguideme.com/step-by-step-guide-to-starting-your-gym-journey-2/covers how cholesterol and blood pressure are interconnected.
By including these external DoFollow links and relevant internal links in your content, you not only provide readers with trustworthy information but also improve SEO, enhance content authority, and help Rank Math recognize your article as a high-quality health resource.
Internal Links Fix – Cholesterol Health
Maintaining good Cholesterol Health involves not only understanding diet and exercise but also learning from related guides on our website. For example, our Heart Health Guide explains how cholesterol affects the heart and blood vessels. Additionally, the Healthy Diet Plan provides tips on reducing LDL and increasing HDL cholesterol naturally. If you want to explore related conditions, the High Blood Pressure Guide shows how cholesterol and blood pressure are interconnected. By including these internal links, readers can easily navigate between related content, improving their experience and ensuring your article is fully SEO optimized.
Maintaining good Cholesterol Health requires accurate information from both trusted external sources and internal guides on our website.
External Resources (DoFollow):
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Global guidelines on cholesterol and heart health: https://www.who.int
- American Heart Association (AHA) – Expert advice on managing LDL and HDL cholesterol: https://www.heart.org
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Research-based information on cholesterol prevention: https://www.cdc.gov
Internal Resources:
- Heart Health Guide – Explains how cholesterol affects the heart and blood vessels:https://healthguideme.com/
- Healthy Diet Plan – Tips to reduce LDL and boost HDL naturally: https://healthguideme.com/ibs-home-remedies/
- High Blood Pressure Guide – Learn how cholesterol and blood pressure are linked: https://healthguideme.com/step-by-step-guide-to-starting-your-gym-journey-2/
high cholesterol
cholesterol symptoms
LDL cholesterol
HDL cholesterol
cholesterol treatment
cholesterol diet
cholesterol management
cholesterol and heart disease