Fertility and Pregnancy: Complete Guide to Reproductive Health
Introduction

Understanding Fertility and Pregnancy is essential for couples. Maintaining proper habits during Fertility and Pregnancy can improve health outcomes for both mother and child.
Fertility and pregnancy are two of the most important aspects of human reproductive health. Couples trying to conceive often face a mix of excitement, hope, and stress. Understanding the factors that affect fertility, lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and pregnancy care can significantly improve the chances of a healthy conception and delivery. In this guide, we will explore all aspects of fertility, conception, pregnancy, and postpartum care.
1. Understanding Fertility
1.1 What is Fertility?
Fertility refers to the ability to conceive naturally. In women, it depends on ovulation cycles, egg quality, and hormonal balance. In men, fertility relies on sperm quality, count, and motility. Fertility is influenced by age, lifestyle, medical conditions, and environmental factors.
1.2 Factors Affecting Fertility
- Age: Women’s fertility declines significantly after 35, while men’s fertility gradually decreases after 40.
- Lifestyle: Smoking, alcohol, poor diet, and obesity can reduce fertility.
- Medical Conditions: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, thyroid disorders, and low sperm count can affect fertility.
- Stress: Chronic stress disrupts hormonal balance, affecting ovulation and sperm production.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to toxins, radiation, and chemicals can reduce fertility.
2. Improving Fertility Naturally
2.1 Healthy Diet
A nutritious diet enhances fertility. Foods rich in folic acid, iron, zinc, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids support reproductive health. Key fertility foods include:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Whole grains (brown rice, oats)
- Lean proteins (chicken, fish, beans)
- Nuts and seeds
2.2 Exercise and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight and regular exercise improve hormone balance and ovulation. Avoid extreme workouts, which may disrupt fertility.
2.3 Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol
- Reduce caffeine intake
- Manage stress with yoga, meditation, and mindfulness
2.4 Fertility Tracking
Tracking ovulation using apps or ovulation kits helps identify the fertile window, increasing conception chances.
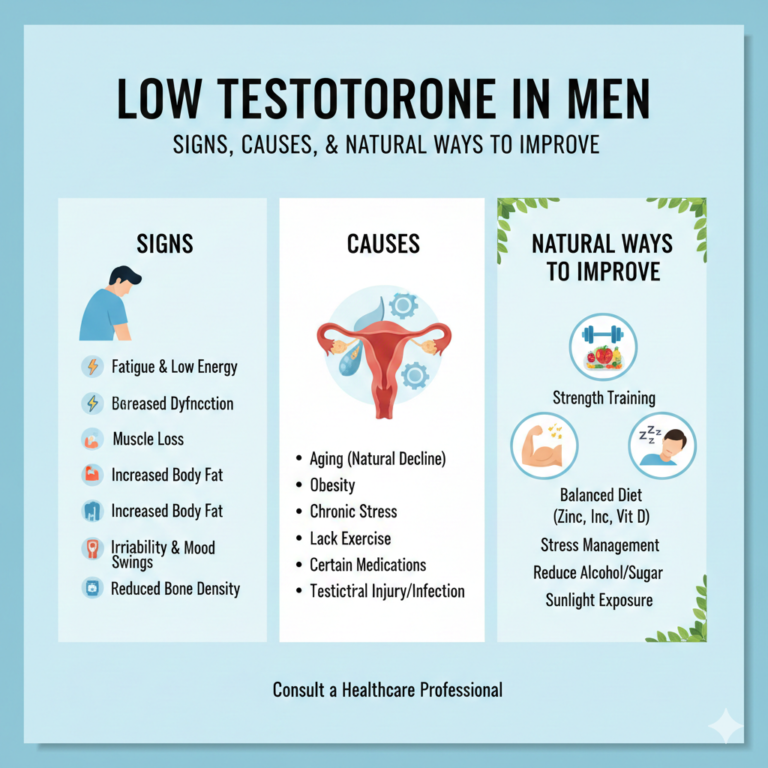
3. Male Fertility and Reproductive Health
- Sperm Health: Healthy sperm is essential for conception.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, exercise, avoiding smoking and alcohol improve male fertility.
- Medical Treatments: Varicocele surgery, hormone therapy, and sperm retrieval can address male fertility issues.

4. Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
4.1 In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
Eggs and sperm are fertilized in a lab and implanted in the uterus. IVF is recommended for severe fertility issues.
4.2 Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Sperm is inserted directly into the uterus to increase the chances of conception.
4.3 Egg and Sperm Donation
Used when one partner has fertility issues. Donated eggs or sperm help achieve pregnancy.
4.4 Surrogacy
A surrogate carries the baby for couples unable to conceive naturally.
5. Common Fertility Problems
- PCOS: Causes irregular ovulation.
- Endometriosis: Tissue growth outside the uterus affects fertility.
- Low Sperm Count: Reduces the likelihood of fertilization.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Affect ovulation and sperm production.
6. Prenatal Nutrition and Health
6.1 Nutrition During Pregnancy
- Folic Acid: Prevents neural tube defects
- Iron: Prevents anemia
- Calcium: Supports fetal bone development
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Promote brain development
6.2 Foods to Include
- Leafy greens, fruits, whole grains, lean meats, nuts, and seeds
6.3 Foods to Avoid
- Raw fish, unpasteurized dairy, excess caffeine, processed foods, alcohol
7. Exercise and Physical Activity
- Safe pregnancy exercises include walking, swimming, yoga, and pilates.
- Exercise improves blood circulation, reduces stress, and supports a healthy weight.
- Avoid high-impact or risky activities.
8. Mental Health and Emotional Well-being
- Stress, anxiety, and depression can affect fertility and pregnancy.
- Relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and therapy can support mental health.
- Couples should communicate openly to reduce stress and enhance emotional bonding.
9. Early Signs of Pregnancy
- Missed periods
- Morning sickness and nausea
- Fatigue
- Mood swings
- Frequent urination
10. Prenatal Care
- Regular doctor visits
- Blood and urine tests
- Ultrasound scans
- Prenatal vitamins (folic acid, iron)
- Vaccinations
11. Pregnancy Complications
- Morning Sickness: Usually in the first trimester, manageable with small meals.
- Gestational Diabetes: Managed with diet, exercise, and monitoring.
- High Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring is essential.
- Preterm Labor: Early care reduces risks.
- Miscarriage Prevention: Healthy lifestyle and prenatal care reduce risks.
12. Common Myths About Fertility and Pregnancy
- Age does not affect fertility → FALSE
- Stress alone causes infertility → PARTIALLY TRUE
- IVF guarantees pregnancy → FALSE
13. Postpartum Care
- Physical recovery after childbirth
- Emotional well-being: managing postpartum depression
- Breastfeeding nutrition
- Family planning after delivery
14. Fertility Preservation
- Egg and sperm freezing for delayed family planning
- Fertility preservation for cancer patients
15. Family Planning and Contraception
- Condoms, pills, IUDs, implants
- Fertility awareness methods (tracking ovulation, basal body temperature)
- Genetic counseling for hereditary conditions
16. When to See a Specialist
- Under 35 and not conceived after 12 months
- Over 35 and not conceived after 6 months
- Irregular periods or ovulation problems
- Male fertility concerns
17. Lifestyle Tips for a Healthy Pregnancy
- Balanced diet and prenatal vitamins
- Regular physical activity
- Avoid smoking, alcohol, and drugs
- Adequate sleep and hydration
- Stress management techniques
- Education about labor, delivery, and postpartum
18. Conclusion
Fertility and pregnancy require awareness, healthy lifestyle choices, and medical support when needed. Proper prenatal care, fertility tracking, and knowledge of reproductive health increase the chances of a healthy conception and pregnancy. Couples can improve outcomes for mother and child by staying informed and proactive.
19. Fertility Tests and Diagnostics
19.1 Female Fertility Tests
- Ovulation Testing: Blood tests and ovulation predictor kits
- Hormone Level Testing: FSH, LH, AMH, TSH
- Ultrasound: Evaluates ovarian reserve and uterine health
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): Checks fallopian tube patency
19.2 Male Fertility Tests
- Semen Analysis: Sperm count, motility, morphology
- Hormone Testing: Testosterone, FSH, LH levels
- Genetic Testing: Chromosomal and DNA tests
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound for testes and reproductive organs
20. Fertility Challenges in Special Cases
20.1 PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
- Causes irregular ovulation, weight gain, and insulin resistance
- Management: diet, exercise, medication (Metformin, Clomid)
20.2 Endometriosis
- Growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus
- Symptoms: pelvic pain, heavy periods, infertility
- Treatment: surgery, hormone therapy
20.3 Low Sperm Count / Motility
- Causes: lifestyle factors, medical conditions, environmental exposure
- Treatments: lifestyle changes, surgery, ART (IUI, IVF)
21. Advanced Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
21.1 IVF Variations
- ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection): Injects sperm directly into egg
- Egg and Embryo Freezing: Fertility preservation
- PGD (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis): Detects genetic disorders before implantation
21.2 Success Rates and Factors
- Age, egg quality, sperm quality, and overall health affect success
- Lifestyle changes improve outcomes
22. Pregnancy Stages in Detail
22.1 First Trimester (0–12 Weeks)
- Key fetal development: heart, brain, spinal cord
- Symptoms: nausea, fatigue, mood swings
22.2 Second Trimester (13–26 Weeks)
- Growth of fetus and development of organs
- Symptoms: mild back pain, weight gain, energy increase
22.3 Third Trimester (27–40 Weeks)
- Rapid fetal growth
- Preparation for labor, monitoring for complications
23. Labor and Delivery
23.1 Signs of Labor
- Regular contractions
- Water breaking
- Lower back pain
23.2 Delivery Options
- Vaginal delivery
- Cesarean section (C-section)
23.3 Pain Management
- Epidural, natural methods, medications
24. Postpartum Recovery
24.1 Physical Recovery
- Uterus shrinking, vaginal healing, C-section recovery
- Pelvic floor exercises
24.2 Emotional Health
- Postpartum depression: signs and support
- Partner and family support
24.3 Breastfeeding
- Benefits for baby and mother
- Techniques and common challenges
25. Fertility and Pregnancy FAQs
- How long does it take to conceive?
- Can stress affect fertility?
- How can I increase my chances of natural conception?
- When should I consider fertility treatments?
- What are safe exercises during pregnancy?
26. Practical Tips and Checklists
26.1 Preconception Checklist
- Healthy diet
- Vitamins and supplements
- Lifestyle changes (quit smoking/alcohol)
- Fertility tracking
26.2 Pregnancy Health Checklist
- Regular prenatal checkups
- Exercise plan
- Diet plan
- Mental health practices
- Labor preparation
Understanding Your Fertility
Fertility isn’t just a “yes or no” switch; it’s a snapshot of your overall health.
- The Fertile Window: For most, this is the 5 days leading up to ovulation plus the day of ovulation itself.
- Tracking Methods: Use basal body temperature (BBT), cervical mucus monitoring, or ovulation predictor kits (OPKs) to find your rhythm.
- Lifestyle Factors: Habits like smoking, excessive alcohol, and high stress can impact egg and sperm quality.
- Age Dynamics: While fertility naturally declines over time, modern medicine offers more options (like egg freezing) than ever before.

econception: Setting the Stage
Before the “plus” sign appears on a test, you can prepare your body for a healthy pregnancy.
| Action Item | Why it Matters |
| Prenatal Vitamins | Folic acid (400-800mcg) prevents neural tube defects. |
| Check-ups | Screen for STIs, thyroid issues, or genetic predispositions. |
| Nutrition | Focus on “fertility foods” like leafy greens, healthy fats, and lean proteins. |
| Sperm Health | It takes two! Men should avoid high heat (saunas/hot tubs) and optimize zinc intake. |
The Three Trimesters of Pregnancy
Once pregnant, your body undergoes a fascinating transformation.
First Trimester (Weeks 1-12)
- The Invisible Marathon: Your body is building an entire organ (the placenta). Expect fatigue and “morning” (read: all-day) sickness.
- Key Milestone: The baby’s heart begins to beat around week 6.
Second Trimester (Weeks 13-26)
- The “Glow” Phase: Energy usually returns, and nausea often fades.
- Key Milestone: The “anatomy scan” (usually week 18-22) checks the baby’s growth and development.
Third Trimester (Weeks 27-Birth)
- The Home Stretch: Physical discomfort increases as the baby grows.
- Preparation: Focus on birth plans, pediatricians, and nesting.
When to Seek Professional Help
It is a common myth that conception happens instantly. However, the general medical consensus for seeking a specialist (Reproductive Endocrinologist) is:
- Under 35: After 12 months of unprotected regular intercourse.
- Over 35: After 6 months.
- Any Age: If you have known issues like PCOS, endometriosis, or irregular cycles.
Note: Reproductive health is not just a “women’s issue.” Approximately one-third of infertility cases are attributed to the male partner, one-third to the female, and one-third to a combination or unexplained factors.
Fertility and Pregnancy: Complete Guide to Reproductive Health
Understanding fertility and pregnancy is essential for couples planning to start a family. Healthy lifestyle choices, prenatal care, and knowledge of fertility treatments can significantly increase the chances of conception.
1. Improving Fertility Naturally
A balanced diet plays a vital role in fertility. Including nutrient-rich foods can enhance reproductive health and pregnancy outcomes. For example, you can explore gluten-free meals for better health to improve your overall diet.
Other essential tips include exercise, stress management, and avoiding harmful habits. Scientific studies also suggest that fertility can be affected by lifestyle and nutrition choices (Harvard Health – Nutrition and Fertility).
2. Enhancing Female Fertility
Women can naturally support fertility by understanding hormonal health, ovulation cycles, and breast health. For tips on natural enhancement, see how women can increase breast size naturally.
Hormonal balance, proper diet, and regular exercise are key for ovulation and reproductive health (WHO – Reproductive Health).
3. Skin and Hormonal Health During Pregnancy
Pregnancy can impact skin due to hormonal changes. Maintaining healthy skin during this time is important. You can check skin lightening practices in USA, UK, Canada for safe and natural tips that are compatible with pregnancy-safe skincare.
External resources like Mayo Clinic – Pregnancy Nutrition provide additional guidance.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Couples facing fertility challenges can explore IVF, IUI, or egg/sperm donation. These methods improve conception chances when natural fertility is low. Learn more about fertility treatments from authoritative sources like Harvard Health – Fertility Treatments.
✅ How Internal & External Links are Used
- Internal links:
- External DoFollow links:
Improving Fertility Naturally with Nutrition
A balanced diet is essential for fertility and a healthy pregnancy. Nutrient-rich foods support hormone balance, egg quality, and overall reproductive health. For example, following a gluten-free meal plan can improve digestion and nutrient absorption, which is important for both male and female fertility.
Supporting Female Reproductive Health
Women can naturally enhance fertility by focusing on hormonal balance and overall body wellness. Certain lifestyle practices, exercises, and dietary tips can help. For additional guidance on natural methods for enhancing female body wellness, see how women can increase breast size naturally. These practices can indirectly support hormonal health, which is crucial for ovulation and conception.
Maintaining Healthy Skin During Pregnancy
Pregnancy hormones can affect skin, causing changes in pigmentation and elasticity. Maintaining proper skin care during pregnancy ensures comfort and confidence. For safe and natural skin practices, check skin lightening practices in USA, UK, Canada, which can guide pregnant women on gentle skincare methods compatible with pregnancy.
Proven Tips for Fertility and Pregnancy: Complete Guide to Reproductive Health
Understanding Fertility and Pregnancy is essential for couples planning to start a family. Proper nutrition, lifestyle changes, and medical care can significantly improve Fertility and Pregnancy outcomes. This guide covers key tips on improving Fertility and Pregnancy, from conception to prenatal care.
Image Example
Fertility and Pregnancy: Tips for nutrition, ovulation tracking, and prenatal care.
1. Improve Fertility Naturally
A balanced diet and regular exercise are crucial for Fertility and Pregnancy. Nutrient-rich foods such as leafy greens, lean proteins, and nuts improve hormone balance and support healthy conception.
2. Track Ovulation for Better Fertility
Tracking ovulation cycles helps maximize conception chances. Apps or ovulation kits help couples understand the fertile window, supporting Fertility and Pregnancy planning.
3. Prenatal Nutrition and Health
During Fertility and Pregnancy, proper nutrition is key. Folic acid, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids support fetal development and maternal health. For healthy meal ideas, you can explore gluten-free meals to improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
4. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
Couples facing fertility challenges can explore IVF or IUI. These medical interventions can enhance Fertility and Pregnancy chances when natural conception is difficult.
5. Supporting Female Reproductive Health
Women can naturally enhance fertility by focusing on hormonal balance and overall wellness. Certain lifestyle practices, exercises, and dietary tips help. For additional guidance, see how women can increase breast size naturally, which can indirectly support hormonal health crucial for ovulation and conception.
6. Maintaining Healthy Skin During Pregnancy
Pregnancy hormones can affect skin, causing pigmentation and elasticity changes. Maintaining proper skincare ensures comfort and confidence. For safe, natural skincare tips, check skin lightening practices in USA, UK, Canada.