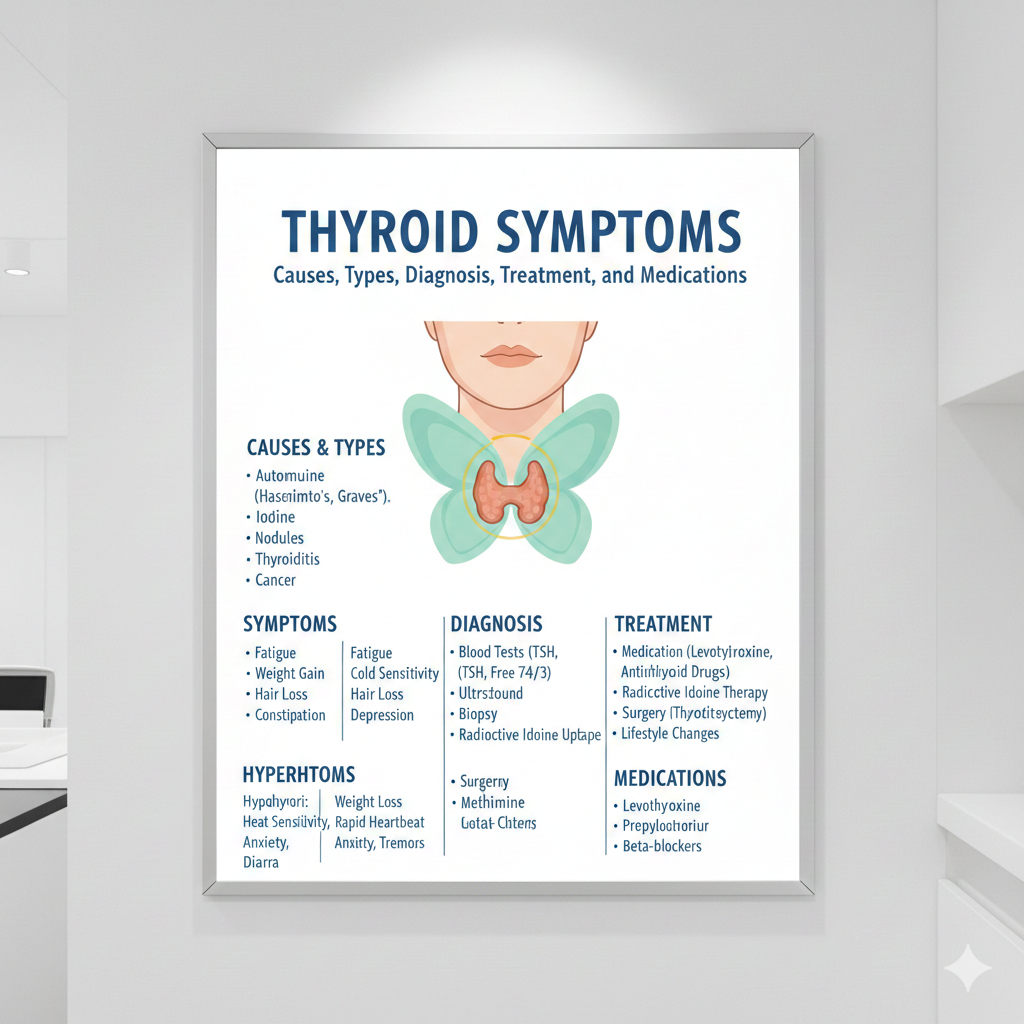
Thyroid Symptoms: Causes, Types, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Medications
Introduction
Thyroid disorders are among the most common hormonal conditions worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. Despite being highly treatable, thyroid problems often remain undiagnosed because their symptoms are gradual, non-specific, and easily confused with other health conditions.
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, body weight, heart rate, and overall hormonal balance. Even a small imbalance in thyroid hormone production can significantly affect physical and mental health.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of thyroid symptoms, including causes, types, diagnostic tests, treatment options, and commonly used medications.
What Is the Thyroid Gland?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located at the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple.
It produces two essential hormones:
- Thyroxine (T4)
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
These hormones regulate:
- Metabolism
- Energy production
- Body temperature
- Heart rate
- Digestion
- Brain development
- Menstrual cycle and fertility
The release of thyroid hormones is controlled by Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), produced by the pituitary gland.
What Is Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid disease occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much or too little thyroid hormone or develops structural abnormalities such as nodules or enlargement.
Thyroid disorders can affect:
- Men and women
- Children and adults
- Pregnant women
However, women are affected 5–8 times more often than men.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones.
Most common cause:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune disease)
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones.
Most common cause:
- Graves’ disease
3. Subclinical Thyroid Disorder
- Mild hormone imbalance
- Few or no symptoms
- Detected mainly through blood tests
4. Goiter and Thyroid Nodules
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Presence of lumps or nodules
- Usually benign, rarely cancerous
Thyroid Symptoms Overview
Thyroid symptoms vary depending on whether hormone levels are low (hypothyroidism) or high (hyperthyroidism).
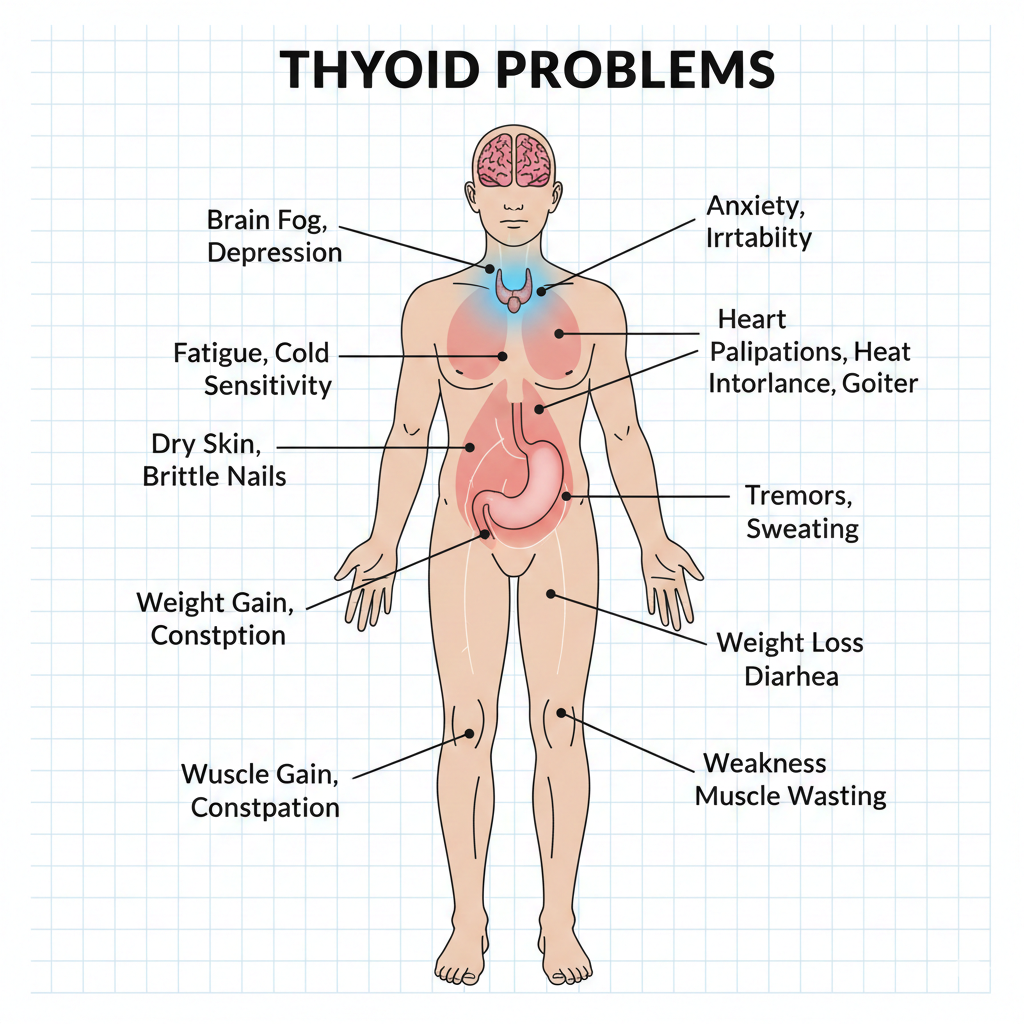
Hypothyroidism Symptoms (Low Thyroid Hormone Levels)
General Symptoms
- Persistent fatigue
- Low energy levels
- Cold intolerance
- Unexplained weight gain
- Slowed metabolism
Physical Symptoms
- Dry, rough skin
- Hair thinning or hair loss
- Brittle nails
- Puffy face
- Swelling of hands and feet
- Hoarse voice
Mental and Emotional Symptoms
- Depression
- Memory problems
- Difficulty concentrating
- Slow thinking
Hypothyroidism Symptoms in Women
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Heavy or prolonged periods
- Infertility
- Pregnancy complications
- Postpartum thyroiditis
- Reduced breast milk production
Hypothyroidism Symptoms in Men
- Decreased libido
- Erectile dysfunction
- Muscle weakness
- Weight gain (especially abdominal fat)
- Low sperm count
- Depression
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms (High Thyroid Hormone Levels)
General Symptoms
- Unintentional weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Heat intolerance
- Excessive sweating
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
Nervous System Symptoms
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Nervousness
- Restlessness
- Insomnia
- Hand tremors
Digestive and Muscle Symptoms
- Frequent bowel movements
- Diarrhea
- Muscle weakness
- Fatigue despite adequate sleep
Eye Symptoms in Graves’ Disease
- Bulging eyes (exophthalmos)
- Dry or irritated eyes
- Double vision
- Sensitivity to light
Thyroid Symptoms in Children and Adolescents
- Delayed growth
- Learning difficulties
- Poor academic performance
- Behavioral changes
- Delayed puberty
- Weight abnormalities
Causes of Thyroid Disorders
Causes of Hypothyroidism
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- Iodine deficiency
- Thyroid surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Certain medications (e.g., lithium)
- Pregnancy-related hormonal changes
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
- Graves’ disease
- Toxic thyroid nodules
- Excess iodine intake
- Overuse of thyroid hormone medication
- Thyroid inflammation (thyroiditis)
Risk Factors for Thyroid Disease
- Female gender
- Family history of thyroid disease
- Pregnancy or recent childbirth
- Autoimmune disorders
- Age over 60
- Excessive iodine intake
Diagnosis of Thyroid Disorders
Blood Tests
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
- Free T3
- Free T4
- Thyroid antibody tests
Imaging Tests
- Thyroid ultrasound
- Radioactive iodine uptake scan
Biopsy
- Fine-needle aspiration (for suspicious nodules)
Thyroid Treatment Options
Treatment depends on:
- Type of thyroid disorder
- Age
- Severity of symptoms
- Pregnancy status
- Coexisting medical conditions
Treatment for Hypothyroidism
Hormone Replacement Therapy
The standard treatment for hypothyroidism is synthetic thyroid hormone replacement.
Common Medications
- Levothyroxine
Brand names:
- Synthroid
- Euthyrox
- Thyronorm
- Eltroxin
- Levoxyl
How it works:
Replaces missing T4 hormone and restores normal metabolic function.
How to take:
- Once daily
- On an empty stomach
- 30–60 minutes before breakfast
Treatment for Hyperthyroidism
Anti-Thyroid Medications
- Methimazole
- Carbimazole
- Propylthiouracil (PTU)
Beta Blockers (Symptom Control)
- Propranolol
- Atenolol
- Metoprolol
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
- Destroys overactive thyroid tissue
- Commonly used for Graves’ disease
- Often results in hypothyroidism requiring lifelong medication
Thyroid Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
Recommended for:
- Large goiter
- Thyroid cancer
- Drug-resistant hyperthyroidism
Thyroid Diet and Nutrition
Beneficial Foods
- Iodized salt
- Eggs
- Fish
- Dairy products
- Nuts
- Whole grains
Foods to Limit
- Excess soy
- Processed foods
- Excess caffeine
- Alcohol
Lifestyle Management
- Regular sleep schedule
- Stress management
- Light to moderate exercise
- Avoid smoking
- Take medications consistently
Thyroid and Pregnancy
- Untreated thyroid disease increases miscarriage risk
- Proper treatment ensures healthy fetal development
- Frequent monitoring required
Complications of Untreated Thyroid Disease
- Heart disease
- Infertility
- Osteoporosis
- Mental health disorders
- Pregnancy complications
When to See a Doctor
- Persistent fatigue
- Unexplained weight changes
- Hair loss
- Irregular periods
- Palpitations
- Neck swelling
Ayurvedic Treatment for Thyroid Disorders
Ayurveda views thyroid disorders as an imbalance of Doshas—primarily Kapha, Vata, and Pitta—along with impaired Agni (digestive fire) and toxin accumulation (Ama).
Ayurvedic treatment focuses on:
- Balancing Doshas
- Improving metabolism
- Detoxifying the body
- Supporting endocrine function
⚠️ Ayurveda is generally used as supportive therapy, not a replacement for conventional medical treatment.
Ayurvedic Medicines for Hypothyroidism
1. Kanchanar Guggulu
Most commonly prescribed Ayurvedic medicine for thyroid
Benefits:
- Supports thyroid gland function
- Reduces gland swelling (goiter)
- Improves metabolism
- Helps with weight gain and sluggishness
Common Use:
Hypothyroidism, thyroid nodules, goiter
2. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera)
Benefits:
- Supports hormone balance
- Reduces stress and cortisol
- Improves energy levels
- May help normalize TSH levels
Best for:
Hypothyroidism with fatigue, stress, anxiety
3. Triphala
Benefits:
- Improves digestion and gut health
- Supports detoxification
- Helps regulate metabolism
- Prevents constipation (common in hypothyroidism)
4. Punarnava
Benefits:
- Reduces swelling and water retention
- Supports kidney and liver detox
- Helpful in puffy face and edema
5. Guggul (Commiphora mukul)
Benefits:
- Enhances fat metabolism
- Supports thyroid hormone activity
- Helps reduce cholesterol
Ayurvedic Medicines for Hyperthyroidism
1. Shankhapushpi
Benefits:
- Calms the nervous system
- Reduces anxiety and restlessness
- Improves sleep quality
2. Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri)
Benefits:
- Reduces mental stress
- Supports cognitive function
- Helps manage irritability and insomnia
3. Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia)
Benefits:
- Balances immunity
- Supports liver function
- Reduces inflammation
4. Praval Pishti
Benefits:
- Helps manage heat intolerance
- Supports calcium balance
- Useful for palpitations and sweating
Ayurvedic Therapies (Panchakarma)
1. Virechana (Therapeutic Purgation)
- Removes excess Pitta and Kapha
- Improves metabolic balance
2. Abhyanga (Oil Massage)
- Reduces stress
- Improves circulation
- Supports hormonal balance
3. Shirodhara
- Relieves anxiety
- Improves sleep
- Calms nervous system
Ayurvedic Diet Recommendations for Thyroid
For Hypothyroidism
- Warm, cooked foods
- Ginger, turmeric, black pepper
- Whole grains
- Avoid cold and processed foods
For Hyperthyroidism
- Cooling foods
- Milk, ghee
- Fresh fruits
- Avoid spicy, salty, and fried foods
Yoga & Pranayama for Thyroid Support
- Sarvangasana (Shoulder Stand)
- Matsyasana (Fish Pose)
- Halasana (Plow Pose)
- Ujjayi Pranayama
- Anulom Vilom
Can Ayurveda Cure Thyroid Disease?
Ayurveda does not guarantee a cure for thyroid disorders.
However, it may:
- Improve symptoms
- Enhance quality of life
- Support metabolism and immunity
- Reduce stress-related hormonal imbalance
Most patients benefit when Ayurveda is used alongside modern medical treatment, under professional supervision.
Safety & Precautions
- Do NOT stop prescribed thyroid medication without doctor approval
- Ayurvedic medicines should be taken under a qualified Ayurvedic physician
- Regular monitoring of TSH, T3, and T4 is essential
- Pregnant women must be extra cautious
Medical Disclaimer (AdSense Friendly)
Ayurvedic treatments mentioned in this article are for informational purposes only. They are not intended to replace professional medical diagnosis or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any herbal or alternative therapy.
Conclusion
Thyroid disease is a common but manageable condition. Early diagnosis, proper treatment, and lifestyle management allow most individuals to live a normal, healthy life.
Awareness of thyroid symptoms is the first step toward timely medical care and long-term well-being.
Yoga for Thyroid Disorders
Yoga plays an important supportive role in managing thyroid disorders by improving blood circulation to the neck region, balancing the endocrine system, reducing stress, and enhancing metabolism.
⚠️ Yoga should be practiced along with medical treatment, not as a replacement.
Best Yoga Asanas for Thyroid Health
1. Sarvangasana (Shoulder Stand)
Benefits:
- Improves blood flow to the thyroid gland
- Stimulates hormone regulation
- Enhances metabolism
Best for:
Hypothyroidism
Duration:
30–60 seconds (2–3 rounds)
⚠️ Avoid if you have neck injury, cervical spondylosis, or high blood pressure.
2. Matsyasana (Fish Pose)
Benefits:
- Stretches the neck and throat region
- Stimulates thyroid and parathyroid glands
- Improves breathing and posture
Best for:
Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism
3. Halasana (Plow Pose)
Benefits:
- Improves circulation to the neck
- Stimulates thyroid secretion
- Helps reduce stress and fatigue
Best for:
Hypothyroidism
4. Bhujangasana (Cobra Pose)
Benefits:
- Strengthens the spine
- Stimulates thyroid function
- Improves digestion and metabolism
Best for:
Hypothyroidism and general hormonal balance
5. Setu Bandhasana (Bridge Pose)
Benefits:
- Gently stretches the neck
- Improves blood flow to thyroid gland
- Reduces anxiety and fatigue
Best for:
Both types of thyroid disorders
6. Dhanurasana (Bow Pose)
Benefits:
- Stimulates endocrine glands
- Improves digestion
- Enhances overall hormonal balance
Best for:
Hypothyroidism
7. Viparita Karani (Legs-Up-The-Wall Pose)
Benefits:
- Calms the nervous system
- Improves circulation
- Reduces stress-related hormonal imbalance
Best for:
Hyperthyroidism, anxiety, insomnia
Pranayama (Breathing Exercises) for Thyroid
1. Ujjayi Pranayama
Benefits:
- Stimulates thyroid gland through gentle throat contraction
- Improves oxygen supply
- Reduces stress
Best for:
Hypothyroidism
2. Anulom Vilom (Alternate Nostril Breathing)
Benefits:
- Balances nervous system
- Reduces stress hormones
- Supports endocrine balance
Best for:
Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism
3. Bhramari Pranayama (Bee Breath)
Benefits:
- Calms mind and body
- Reduces anxiety and palpitations
- Improves sleep
Best for:
Hyperthyroidism
4. Sheetali & Sheetkari Pranayama
Benefits:
- Cooling effect on the body
- Reduces heat intolerance and sweating
Best for:
Hyperthyroidism
Recommended Yoga Routine for Thyroid (Beginner-Friendly)
Daily Practice (20–30 minutes):
- Anulom Vilom – 5 minutes
- Bhujangasana – 3 rounds
- Setu Bandhasana – 3 rounds
- Sarvangasana + Matsyasana – 2 rounds
- Bhramari – 5 repetitions
- Shavasana – 5 minutes
Yoga Precautions for Thyroid Patients
- Practice yoga on an empty stomach
- Avoid overstraining the neck
- Stop immediately if dizziness or pain occurs
- Pregnant women should consult a doctor/yoga therapist
- Continue prescribed thyroid medication
Can Yoga Cure Thyroid Disorders?
Yoga cannot cure thyroid disease, but regular practice may:
- Improve symptoms
- Reduce stress-related hormone imbalance
- Support metabolism and energy levels
- Improve quality of life
Best results are achieved when yoga is combined with:
- Medical treatment
- Proper diet
- Stress management
🔗 1️⃣ Homepage Link
URL:
https://healthguideme.com/
Where to place: Introduction / Conclusion
Sentence (use one):
For more trusted health guides and medical information, visit our main health resource at Health Guide Me.
Anchor text:
Health Guide Me
🔗 2️⃣ Heart Disease Article Link
URL:
https://healthguideme.com/heart-disease-treatment-options/
Where to place:
Complications / Risk Factors / Untreated Thyroid section
Sentence:
Untreated thyroid disorders may increase the risk of cardiovascular problems, including conditions discussed in our guide on heart disease treatment options.
Anchor text:
heart disease treatment options
🔗 3️⃣ Fatty Liver Disease Article Link
URL:
https://healthguideme.com/fatty-liver-disease-genetics/
Where to place:
Causes / Metabolism / Weight Gain section
Sentence:
Thyroid-related metabolic imbalance can also affect liver health, and studies suggest a link with conditions such as fatty liver disease influenced by genetics.
Anchor text:
fatty liver disease influenced by genetics
Medical Disclaimer
Yoga practices mentioned in this article are for educational purposes only. Always consult a qualified yoga instructor or healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine, especially if you have a thyroid disorder.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice.
thyroid symptoms, hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, thyroid treatment, thyroid medicine, thyroid ayurveda, yoga for thyroid, hormonal imbalance
Thyroid Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Thyroid disease is a common hormonal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, heart rate, and body temperature. When the thyroid gland does not function properly, it can lead to a wide range of physical and mental health problems.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), iodine deficiency remains one of the leading global causes of thyroid disorders, particularly in developing countries.
(Source: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/iodine-deficiency)
What Is Thyroid Disease?
Thyroid disease occurs when the thyroid gland produces either too much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or too little hormone (hypothyroidism). Both conditions can significantly impact overall health if left untreated.
The Mayo Clinic explains that thyroid disorders affect metabolism and can influence weight, heart function, mood, and energy levels.
(Source: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/thyroid-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20351897)
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. It is more common in women and often develops slowly.
Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Depression and memory problems
According to the NHS (UK), hypothyroidism is a long-term condition that can usually be controlled well with daily hormone replacement medication.
(Source: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/underactive-thyroid-hypothyroidism/)
Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces excessive hormones, speeding up the body’s metabolism.
Common symptoms include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Weight loss despite increased appetite
- Anxiety and irritability
- Excessive sweating
- Tremors
Causes of Thyroid Disease
Several factors can contribute to thyroid disorders, including:
- Iodine deficiency
- Autoimmune diseases such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Graves’ disease
- Genetics
- Pregnancy-related hormonal changes
- Certain medications
Research shows that metabolic and hormonal imbalances linked to thyroid disease may also increase the risk of cardiovascular and liver-related conditions.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Disorders
Doctors diagnose thyroid disease using physical examinations and blood tests. The most commonly used tests include:
- TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone)
- T3 and T4 hormone levels
According to MedlinePlus, these blood tests are essential for determining whether the thyroid gland is overactive or underactive and for guiding treatment decisions.
(Source: https://medlineplus.gov/thyroidtests.html)
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disease
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the thyroid disorder.
- Hypothyroidism is typically treated with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement.
- Hyperthyroidism may be treated with medication, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery in severe cases.
Medical experts emphasize the importance of regular monitoring to maintain healthy hormone levels and prevent complications such as heart disease and infertility.
Lifestyle and Prevention Tips
While not all thyroid conditions can be prevented, the following steps may help support thyroid health:
- Ensure adequate iodine intake through diet
- Manage stress effectively
- Maintain a balanced diet
- Get regular medical checkups
- Follow prescribed treatments consistently
The World Health Organization highlights that public awareness and early detection are key strategies in reducing the global burden of thyroid disease.
(Source: https://www.who.int)
Conclusion
Thyroid disease is a manageable condition when diagnosed early and treated properly. Trusted global health authorities such as the WHO, Mayo Clinic, NHS, and MedlinePlus agree that timely medical care, regular monitoring, and patient education are essential for maintaining long-term health and preventing complications related to thyroid dysfunction.